A Systematic Literature Review of Automated Query Reformulations in Source Code Search
Paper and Code
Aug 22, 2021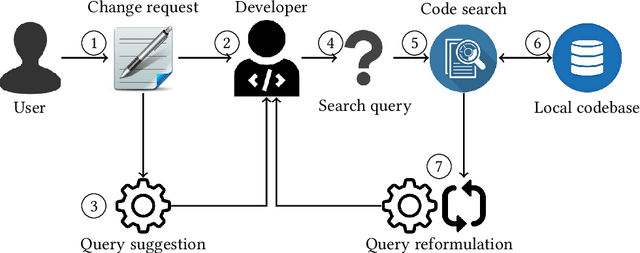
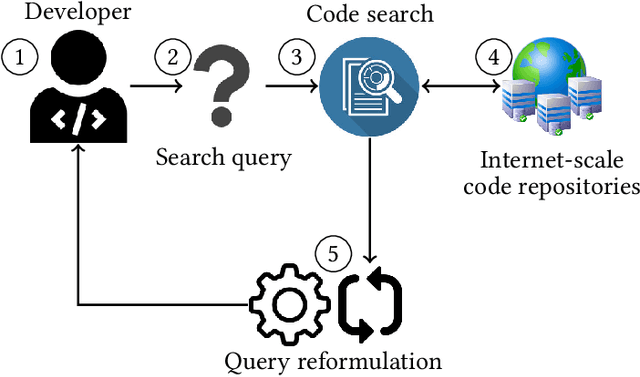

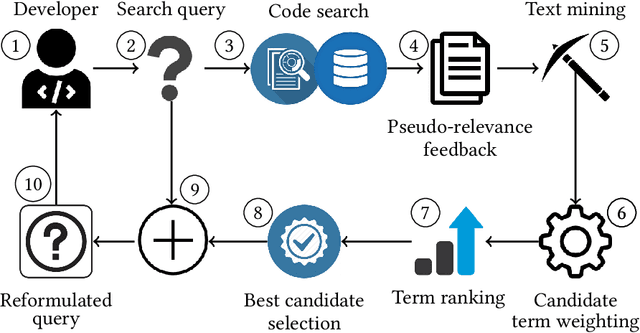
Software developers often fix critical bugs to ensure the reliability of their software. They might also need to add new features to their software at a regular interval to stay competitive in the market. These bugs and features are reported as change requests (i.e., technical documents written by software users). Developers consult these documents to implement the required changes in the software code. As a part of change implementation, they often choose a few important keywords from a change request as an ad hoc query. Then they execute the query with a code search engine (e.g., Lucene) and attempt to find out the exact locations within the software code that need to be changed. Unfortunately, even experienced developers often fail to choose the right queries. As a consequence, the developers often experience difficulties in detecting the appropriate locations within the code and spend the majority of their time in numerous trials and errors. There have been many studies that attempt to support developers in constructing queries by automatically reformulating their ad hoc queries. In this systematic literature review, we carefully select 70 primary studies on query reformulations from 2,970 candidate studies, perform an in-depth qualitative analysis using the Grounded Theory approach, and then answer six important research questions. Our investigation has reported several major findings. First, to date, eight major methodologies (e.g., term weighting, query-term co-occurrence analysis, thesaurus lookup) have been adopted in query reformulation. Second, the existing studies suffer from several major limitations (e.g., lack of generalizability, vocabulary mismatch problem, weak evaluation, the extra burden on the developers) that might prevent their wide adoption. Finally, we discuss several open issues in search query reformulations and suggest multiple future research opportunities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge