A Semi-automatic Cell Tracking Process Towards Completing the 4D Atlas of C. elegans Development
Paper and Code
Aug 02, 2022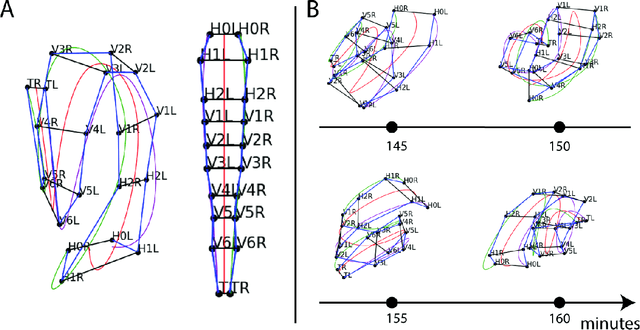
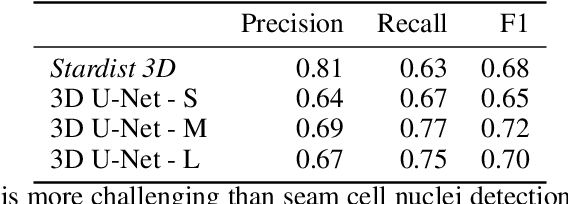
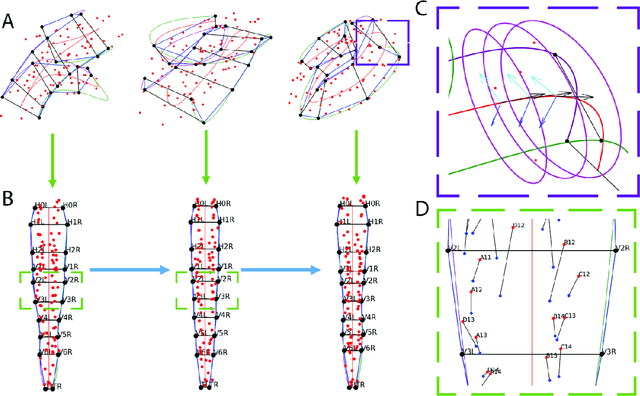
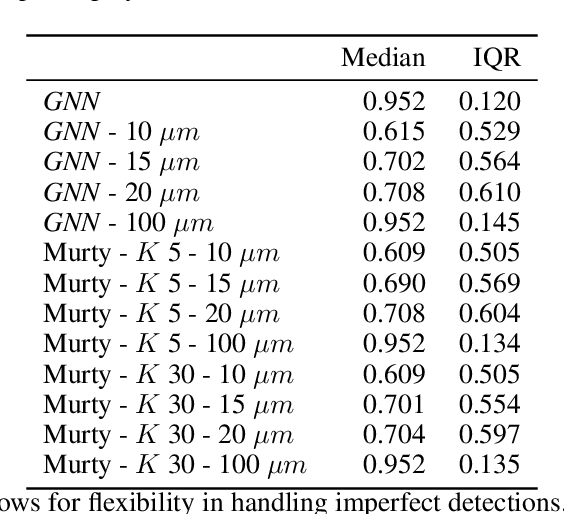
The nematode Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) is used as a model organism to better understand developmental biology and neurobiology. C. elegans features an invariant cell lineage, which has been catalogued and observed using fluorescence microscopy images. However, established methods to track cells in late-stage development fail to generalize once sporadic muscular twitching has begun. We build upon methodology which uses skin cells as fiducial markers to carry out cell tracking despite random twitching. In particular, we present a cell nucleus segmentation and tracking procedure which was integrated into a 3D rendering GUI to improve efficiency in tracking cells across late-stage development. Results on images depicting aforementioned muscle cell nuclei across three test embryos suggest the fiducial markers in conjunction with a classic tracking paradigm overcome sporadic twitching.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge