A Relational Inductive Bias for Dimensional Abstraction in Neural Networks
Paper and Code
Feb 28, 2024
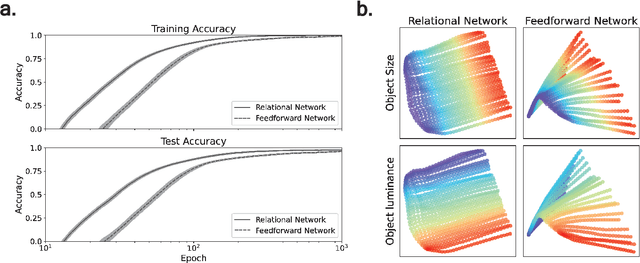
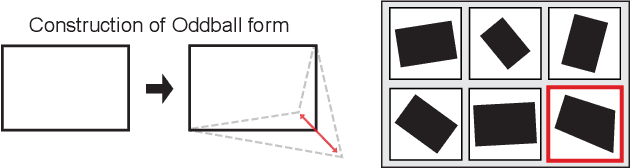
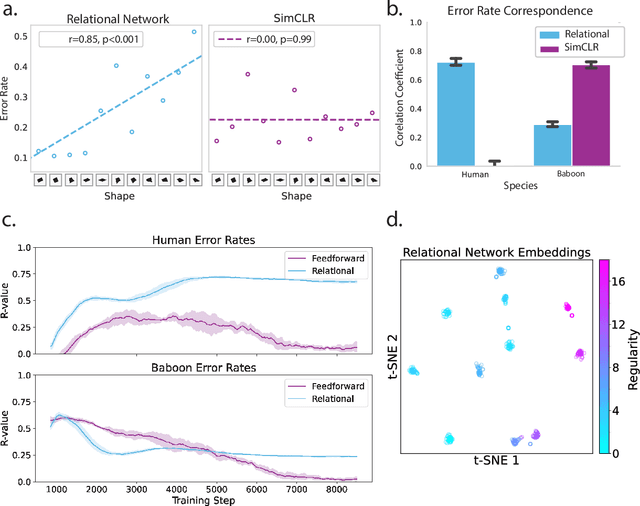
The human cognitive system exhibits remarkable flexibility and generalization capabilities, partly due to its ability to form low-dimensional, compositional representations of the environment. In contrast, standard neural network architectures often struggle with abstract reasoning tasks, overfitting, and requiring extensive data for training. This paper investigates the impact of the relational bottleneck -- a mechanism that focuses processing on relations among inputs -- on the learning of factorized representations conducive to compositional coding and the attendant flexibility of processing. We demonstrate that such a bottleneck not only improves generalization and learning efficiency, but also aligns network performance with human-like behavioral biases. Networks trained with the relational bottleneck developed orthogonal representations of feature dimensions latent in the dataset, reflecting the factorized structure thought to underlie human cognitive flexibility. Moreover, the relational network mimics human biases towards regularity without pre-specified symbolic primitives, suggesting that the bottleneck fosters the emergence of abstract representations that confer flexibility akin to symbols.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge