A Real-Time Voice Activity Detection Based On Lightweight Neural
Paper and Code
May 27, 2024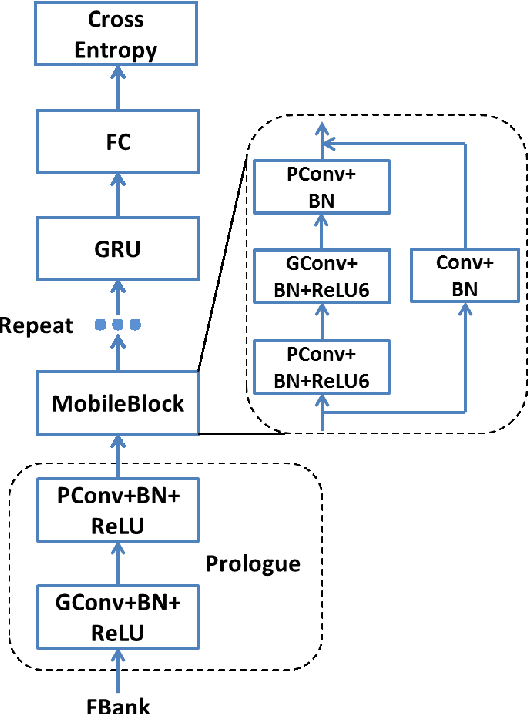
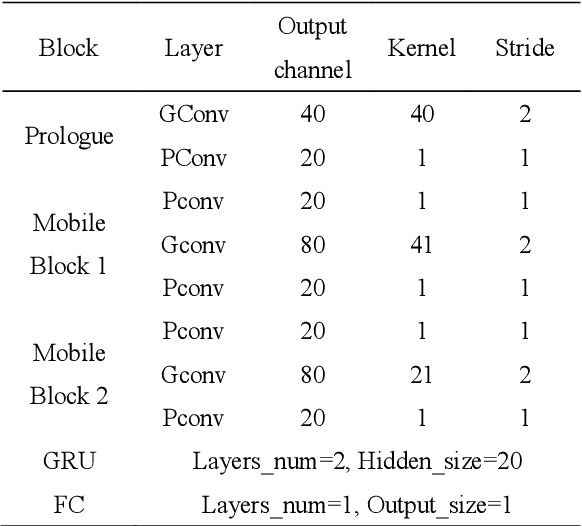
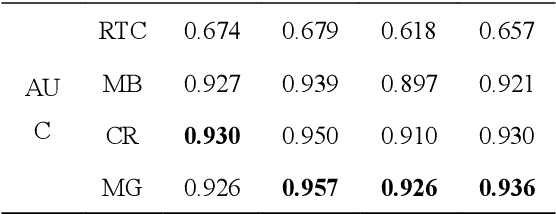
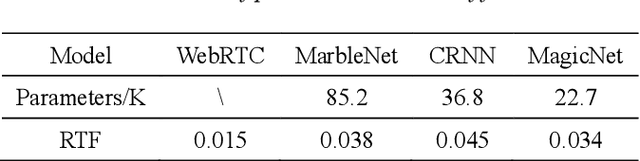
Voice activity detection (VAD) is the task of detecting speech in an audio stream, which is challenging due to numerous unseen noises and low signal-to-noise ratios in real environments. Recently, neural network-based VADs have alleviated the degradation of performance to some extent. However, the majority of existing studies have employed excessively large models and incorporated future context, while neglecting to evaluate the operational efficiency and latency of the models. In this paper, we propose a lightweight and real-time neural network called MagicNet, which utilizes casual and depth separable 1-D convolutions and GRU. Without relying on future features as input, our proposed model is compared with two state-of-the-art algorithms on synthesized in-domain and out-domain test datasets. The evaluation results demonstrate that MagicNet can achieve improved performance and robustness with fewer parameter costs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge