A Quantitative Analysis of Physical Security and Path Loss With Frequency for IBOB Channel
Paper and Code
Apr 27, 2022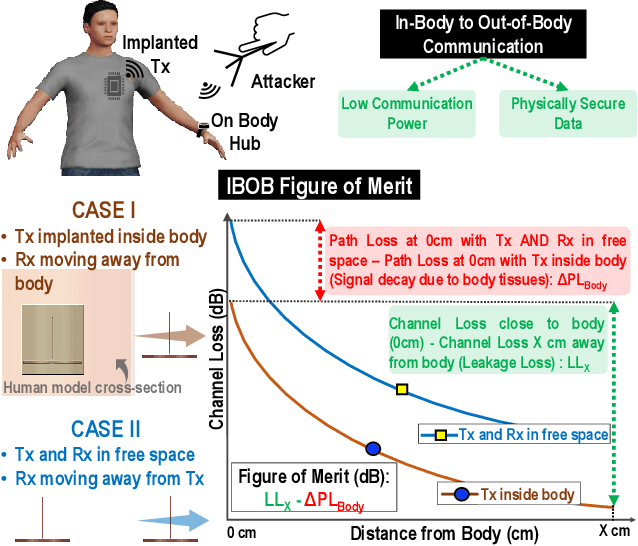
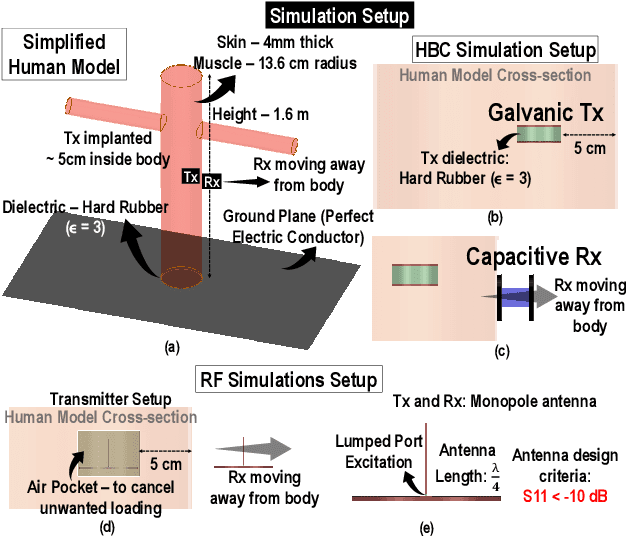
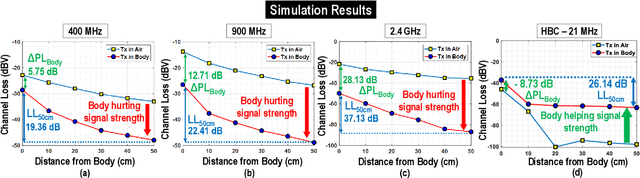
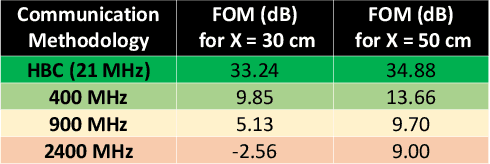
Security vulnerabilities demonstrated in implantable medical devices have opened the door for research into physically secure and low power communication methodologies. In this study, we perform a comparative analysis of commonly used ISM frequency bands and human body communication (HBC) for data transfer from in-body to out-of-body (IBOB). We develop a figure of merit (FoM) that comprises of the critical parameters to quantitatively compare the communication methodologies. We perform finite-element method (FEM)-based simulations and experiments to validate the FoM developed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge