A Probabilistic Model Of Interaction Dynamics for Dyadic Face-to-Face Settings
Paper and Code
Jul 10, 2022
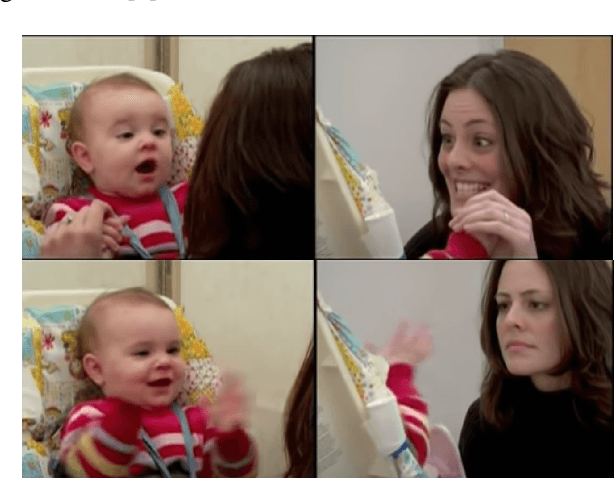
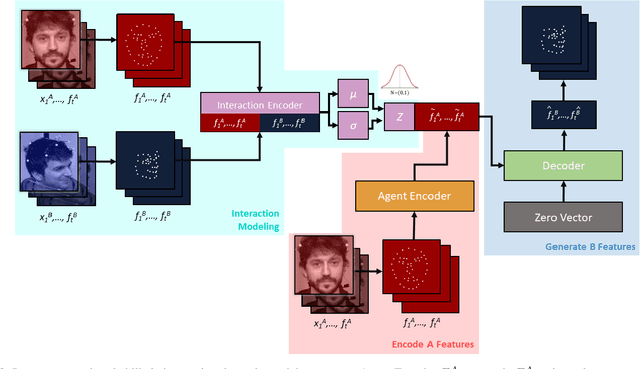


Natural conversations between humans often involve a large number of non-verbal nuanced expressions, displayed at key times throughout the conversation. Understanding and being able to model these complex interactions is essential for creating realistic human-agent communication, whether in the virtual or physical world. As social robots and intelligent avatars emerge in popularity and utility, being able to realistically model and generate these dynamic expressions throughout conversations is critical. We develop a probabilistic model to capture the interaction dynamics between pairs of participants in a face-to-face setting, allowing for the encoding of synchronous expressions between the interlocutors. This interaction encoding is then used to influence the generation when predicting one agent's future dynamics, conditioned on the other's current dynamics. FLAME features are extracted from videos containing natural conversations between subjects to train our interaction model. We successfully assess the efficacy of our proposed model via quantitative metrics and qualitative metrics, and show that it successfully captures the dynamics of a pair of interacting dyads. We also test the model with a never-before-seen parent-infant dataset comprising of two different modes of communication between the dyads, and show that our model successfully delineates between the modes, based on their interacting dynamics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge