A Novel Q-stem Connected Architecture for Beyond-Diagonal Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces
Paper and Code
Nov 27, 2024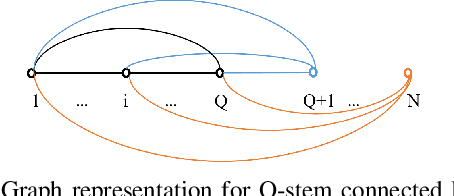
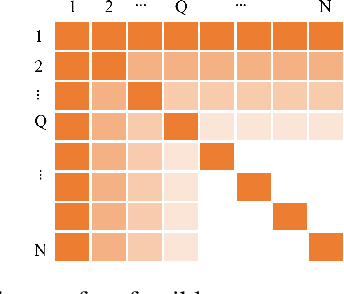
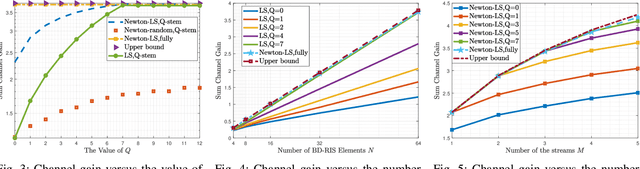
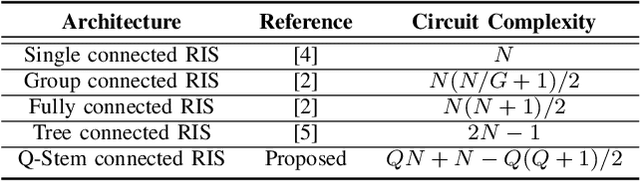
Beyond-diagonal reconfigurable intelligent surface (BD-RIS) has garnered significant research interest recently due to its ability to generalize existing reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) architectures and provide enhanced performance through flexible inter-connection among RIS elements. However, current BD-RIS designs often face challenges related to high circuit complexity and computational complexity, and there is limited study on the trade-off between system performance and circuit complexity. To address these issues, in this work, we propose a novel BD-RIS architecture named Q-stem connected RIS that integrates the characteristics of existing single connected, tree connected, and fully connected BD-RIS, facilitating an effective trade-off between system performance and circuit complexity. Additionally, we propose two algorithms to design the RIS scattering matrix for a Q-stem connected RIS aided multi-user broadcast channels, namely, a low-complexity least squares (LS) algorithm and a suboptimal LS-based quasi-Newton algorithm. Simulations show that the proposed architecture is capable of attaining the sum channel gain achieved by fully connected RIS while reducing the circuit complexity. Moreover, the proposed LS-based quasi-Newton algorithm significantly outperforms the baselines, while the LS algorithm provides comparable performance with a substantial reduction in computational complexity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge