A Novel Framework for Robustness Analysis of Visual QA Models
Paper and Code
Nov 19, 2017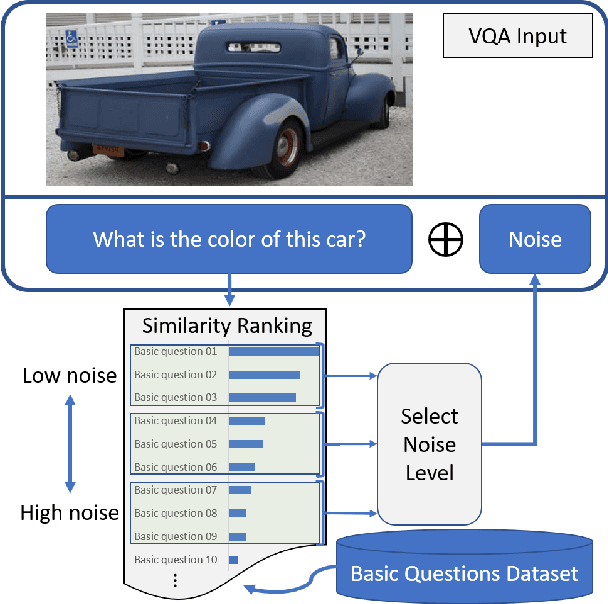
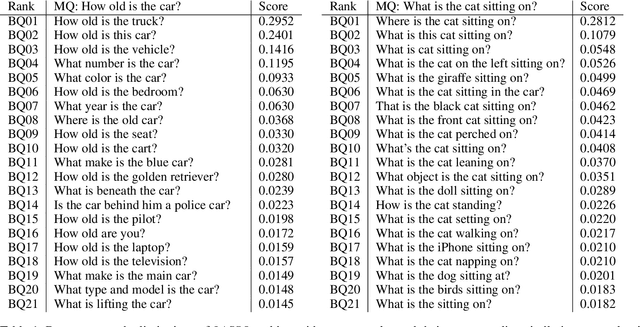
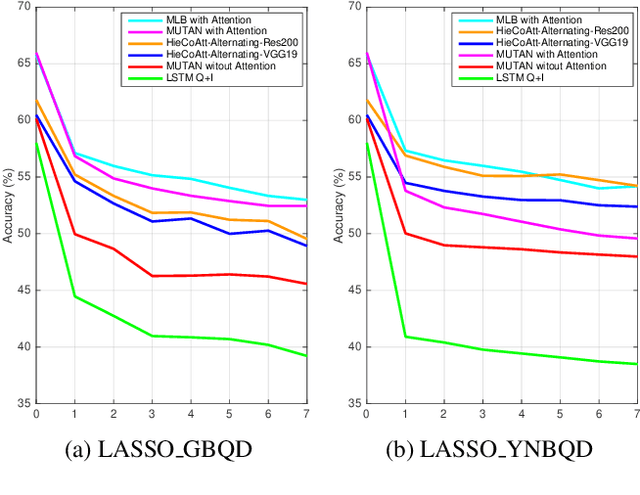
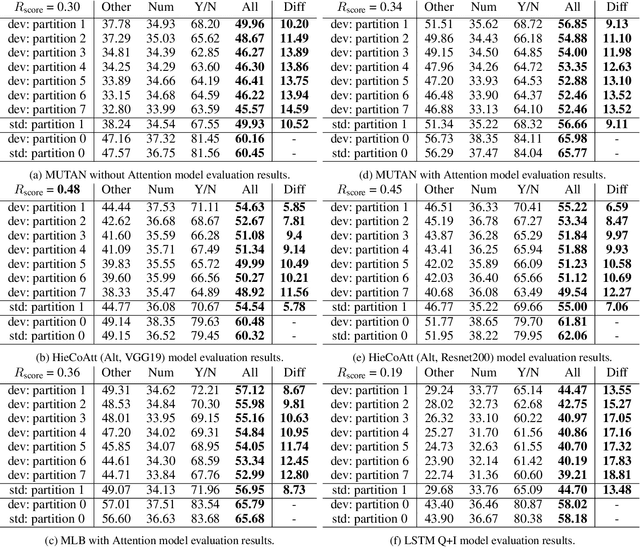
Deep neural networks have been playing an essential role in many computer vision tasks including Visual Question Answering (VQA). Until recently, the study of their accuracy has been the main focus of research and now there is a huge trend toward assessing the robustness of these models against adversarial attacks by evaluating the accuracy of these models under increasing levels of noisiness. In VQA, the attack can target the image and/or the proposed main question and yet there is a lack of proper analysis of this aspect of VQA. In this work, we propose a new framework that uses semantically relevant questions, dubbed basic questions, acting as noise to evaluate the robustness of VQA models. We hypothesize that as the similarity of a basic question to the main question decreases, the level of noise increases. So, to generate a reasonable noise level for a given main question, we rank a pool of basic questions based on their similarity with this main question. We cast this ranking problem as a LASSO optimization problem. We also propose a novel robustness measure R_score and two large-scale question datasets, General Basic Question Dataset and Yes/No Basic Question Dataset in order to standardize robustness analysis of VQA models. We analyze the robustness of several state-of-the-art VQA models and show that attention-based VQA models are more robust than other methods in general. The main goal of this framework is to serve as a benchmark to help the community in building more accurate and robust VQA models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge