A Note on Geometric Calibration of Multiple Cameras and Projectors
Paper and Code
Oct 24, 2024
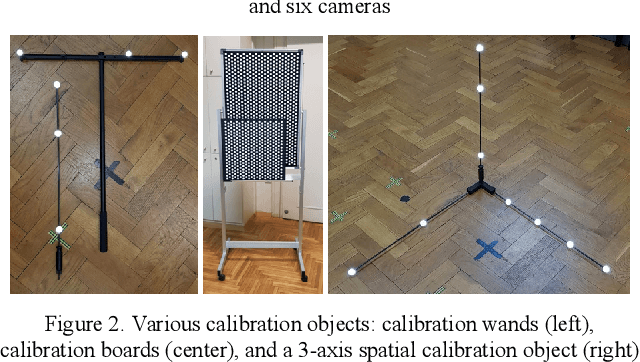


Geometric calibration of cameras and projectors is an essential step that must be performed before any imaging system can be used. There are many well-known geometric calibration methods for calibrating systems comprised of multiple cameras, but simultaneous geometric calibration of multiple projectors and cameras has received less attention. This leaves unresolved several practical issues which must be considered to achieve the simplicity of use required for real world applications. In this work we discuss several important components of a real-world geometric calibration procedure used in our laboratory to calibrate surface imaging systems comprised of many projectors and cameras. We specifically discuss the design of the calibration object and the image processing pipeline used to analyze it in the acquired images. We also provide quantitative calibration results in the form of reprojection errors and compare them to the classic approaches such as Zhang's calibration method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge