A New Non-Negative Matrix Factorization Approach for Blind Source Separation of Cardiovascular and Respiratory Sound Based on the Periodicity of Heart and Lung Function
Paper and Code
May 03, 2023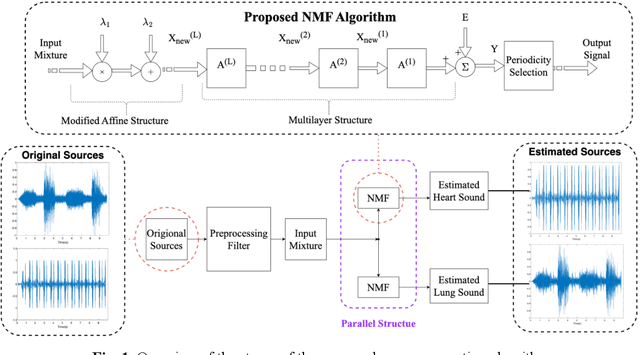
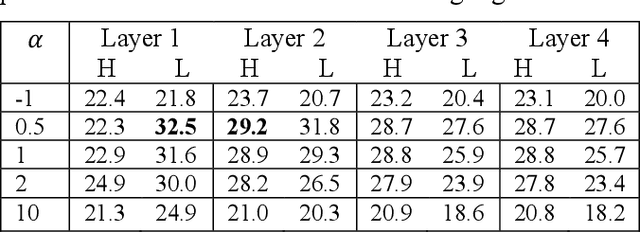
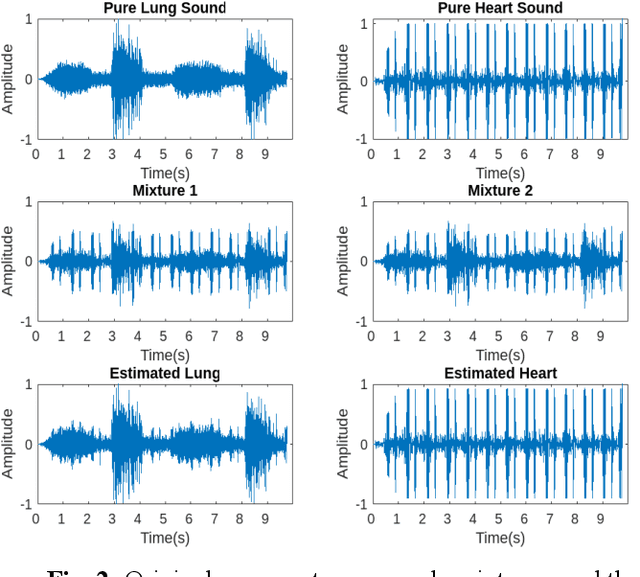
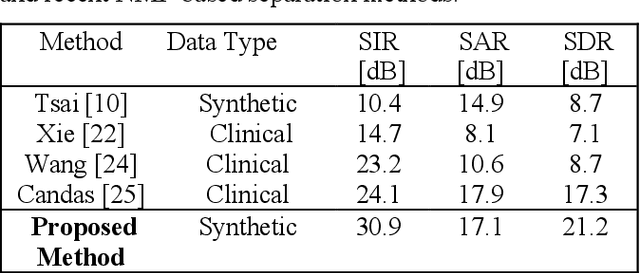
Auscultation provides a rich diversity of information to diagnose cardiovascular and respiratory diseases. However, sound auscultation is challenging due to noise. In this study, a modified version of the affine non-negative matrix factorization (NMF) approach is proposed to blindly separate lung and heart sounds recorded by a digital stethoscope. This method applies a novel NMF algorithm, which embodies a parallel structure of multilayer units on the input signal, to find a proper estimation of source signals. Another key innovation is the use of the periodic property of the signals which improves accuracy compared to previous works. The method is tested on 100 cases. Each case consists of two synthesized mixtures of real measurements. The effect of different parameters is discussed, and the results are compared to other current methods. Results demonstrate improvements in the source-to-distortion ratio (SDR), source-to-interference ratio (SIR), and source-to-artifacts ratio (SAR) of heart and lung sounds, respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge