A Multi-Disciplinary Review of Knowledge Acquisition Methods: From Human to Autonomous Eliciting Agents
Paper and Code
Feb 27, 2018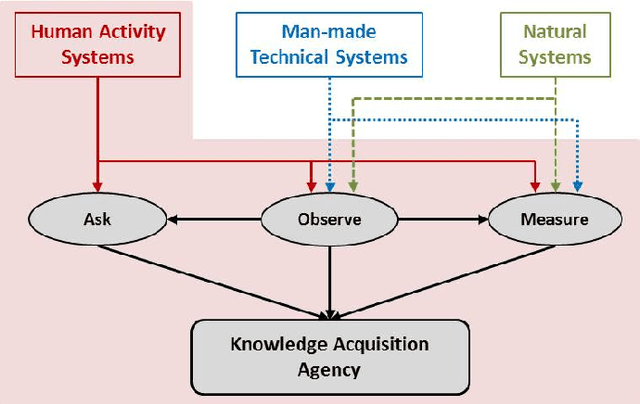
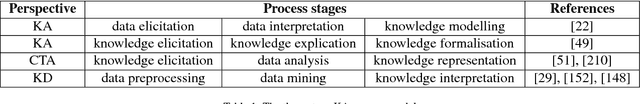
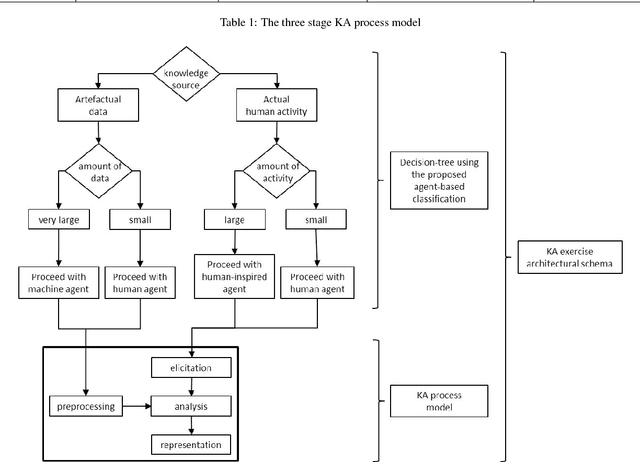
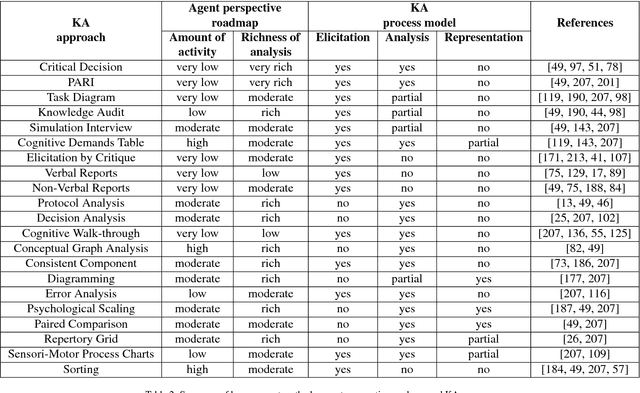
This paper offers a multi-disciplinary review of knowledge acquisition methods in human activity systems. The review captures the degree of involvement of various types of agencies in the knowledge acquisition process, and proposes a classification with three categories of methods: the human agent, the human-inspired agent, and the autonomous machine agent methods. In the first two categories, the acquisition of knowledge is seen as a cognitive task analysis exercise, while in the third category knowledge acquisition is treated as an autonomous knowledge-discovery endeavour. The motivation for this classification stems from the continuous change over time of the structure, meaning and purpose of human activity systems, which are seen as the factor that fuelled researchers' and practitioners' efforts in knowledge acquisition for more than a century. We show through this review that the KA field is increasingly active due to the higher and higher pace of change in human activity, and conclude by discussing the emergence of a fourth category of knowledge acquisition methods, which are based on red-teaming and co-evolution.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge