A message-passing algorithm for multi-agent trajectory planning
Paper and Code
Nov 18, 2013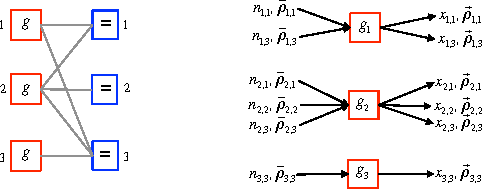
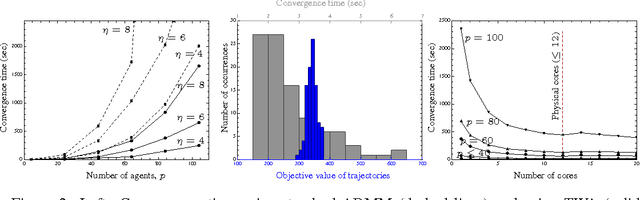
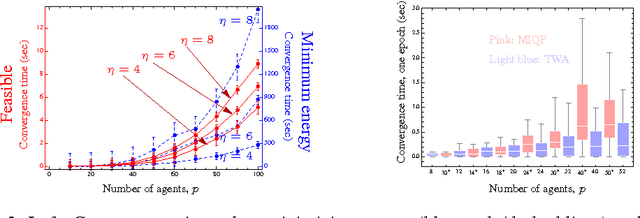
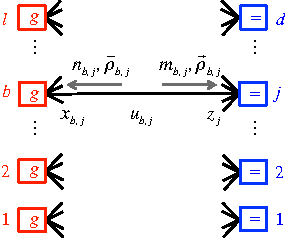
We describe a novel approach for computing collision-free \emph{global} trajectories for $p$ agents with specified initial and final configurations, based on an improved version of the alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM). Compared with existing methods, our approach is naturally parallelizable and allows for incorporating different cost functionals with only minor adjustments. We apply our method to classical challenging instances and observe that its computational requirements scale well with $p$ for several cost functionals. We also show that a specialization of our algorithm can be used for {\em local} motion planning by solving the problem of joint optimization in velocity space.
* In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), 2013.
Demo video available at http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yuGCkVT8Bew
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge