A learning perspective on the emergence of abstractions: the curious case of phonemes
Paper and Code
Dec 17, 2020
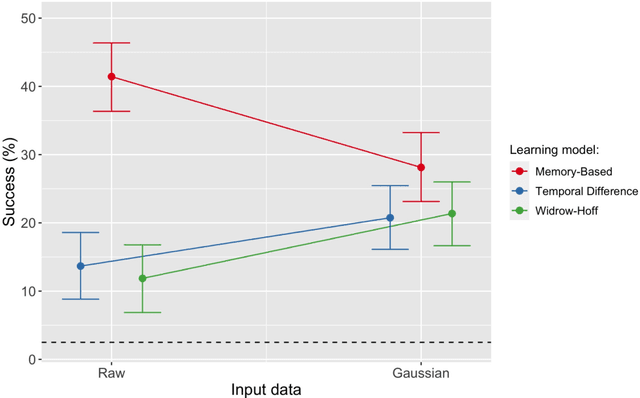


In the present paper we use a range of modeling techniques to investigate whether an abstract phone could emerge from exposure to speech sounds. We test two opposing principles regarding the development of language knowledge in linguistically untrained language users: Memory-Based Learning (MBL) and Error-Correction Learning (ECL). A process of generalization underlies the abstractions linguists operate with, and we probed whether MBL and ECL could give rise to a type of language knowledge that resembles linguistic abstractions. Each model was presented with a significant amount of pre-processed speech produced by one speaker. We assessed the consistency or stability of what the models have learned and their ability to give rise to abstract categories. Both types of models fare differently with regard to these tests. We show that ECL learning models can learn abstractions and that at least part of the phone inventory can be reliably identified from the input.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge