A Learning Framework for Diffeomorphic Image Registration based on Quasi-conformal Geometry
Paper and Code
Oct 20, 2021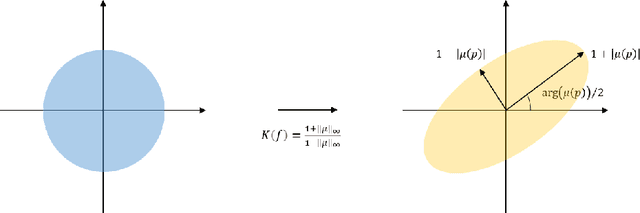
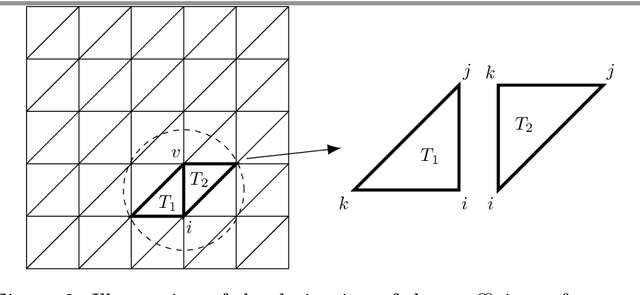
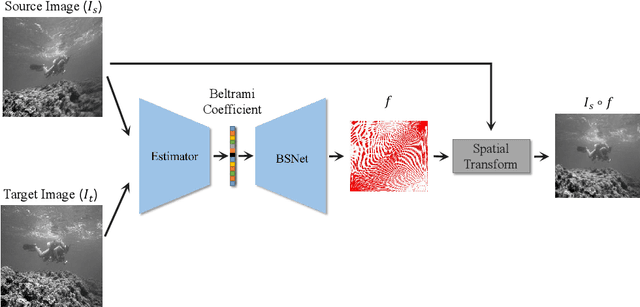
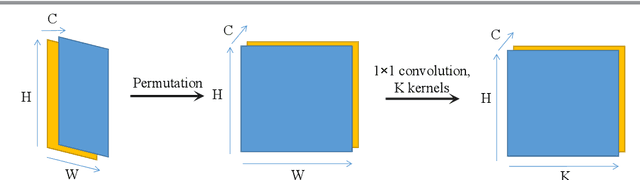
Image registration, the process of defining meaningful correspondences between images, is essential for various image analysis tasks, especially medical imaging. Numerous learning-based methods, notably convolutional neural networks (CNNs), for deformable image registration proposed in recent years have demonstrated the feasibility and superiority of deep learning techniques for registration problems. Besides, compared to traditional algorithms' optimization scheme of the objective function for each image pair, learning-based algorithms are several orders of magnitude faster. However, these data-driven methods without proper constraint on the deformation field will easily lead to topological foldings. To tackle this problem, We propose the quasi-conformal registration network (QCRegNet), an unsupervised learning framework, to obtain diffeomorphic 2D image registrations with large deformations based on quasi-conformal (QC) map, an orientation-preserving homeomorphism between two manifolds. The basic idea is to design a CNN mapping image pairs to deformation fields. QCRegNet consists of the estimator network and the Beltrami solver network (BSNet). The estimator network takes image pair as input and outputs the Beltrami coefficient (BC). The BC, which captures conformal distortion of a QC map and guarantees the bijectivity, will then be input to the BSNet, a task-independent network which reconstructs the desired QC map. Furthermore, we reduce the number of network parameters and computational complexity by utilizing Fourier approximation to compress BC. Experiments have been carried out on different data such as underwater and medical images. Registration results show that the registration accuracy is comparable to state-of-the-art methods and diffeomorphism is to a great extent guaranteed compared to other diffeomorphic registration algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge