A Latent Source Model for Nonparametric Time Series Classification
Paper and Code
Dec 13, 2013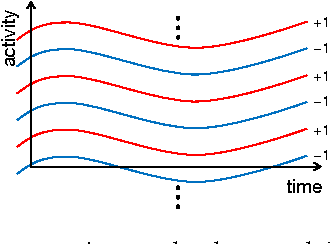
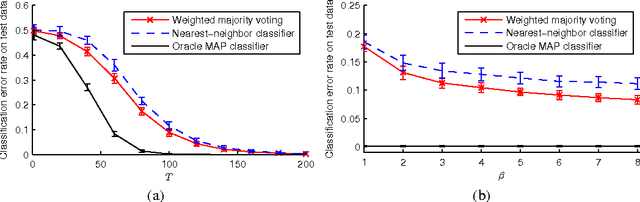
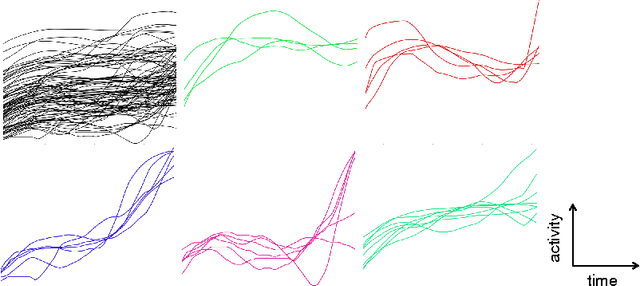
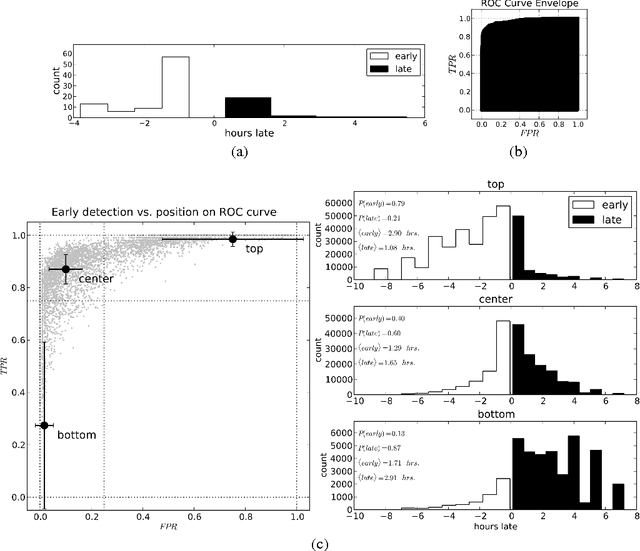
For classifying time series, a nearest-neighbor approach is widely used in practice with performance often competitive with or better than more elaborate methods such as neural networks, decision trees, and support vector machines. We develop theoretical justification for the effectiveness of nearest-neighbor-like classification of time series. Our guiding hypothesis is that in many applications, such as forecasting which topics will become trends on Twitter, there aren't actually that many prototypical time series to begin with, relative to the number of time series we have access to, e.g., topics become trends on Twitter only in a few distinct manners whereas we can collect massive amounts of Twitter data. To operationalize this hypothesis, we propose a latent source model for time series, which naturally leads to a "weighted majority voting" classification rule that can be approximated by a nearest-neighbor classifier. We establish nonasymptotic performance guarantees of both weighted majority voting and nearest-neighbor classification under our model accounting for how much of the time series we observe and the model complexity. Experimental results on synthetic data show weighted majority voting achieving the same misclassification rate as nearest-neighbor classification while observing less of the time series. We then use weighted majority to forecast which news topics on Twitter become trends, where we are able to detect such "trending topics" in advance of Twitter 79% of the time, with a mean early advantage of 1 hour and 26 minutes, a true positive rate of 95%, and a false positive rate of 4%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge