A Hybrid Approach for Low-Complexity Joint Acoustic Echo and Noise Reduction
Paper and Code
Aug 28, 2024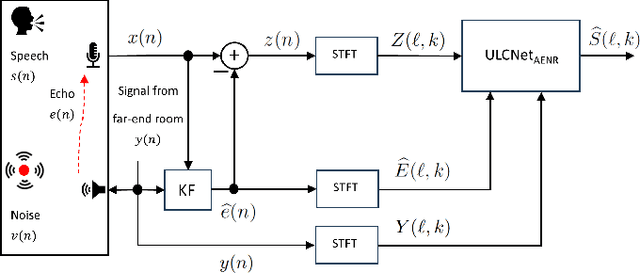

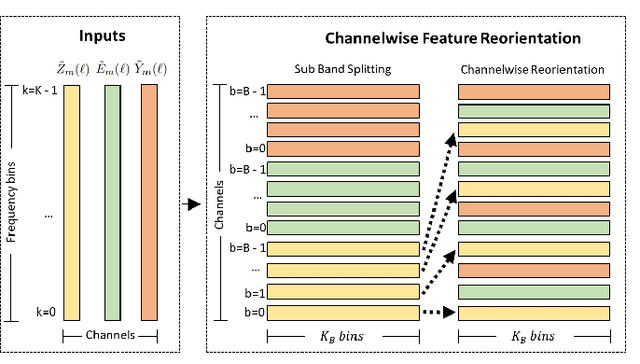

Deep learning-based methods that jointly perform the task of acoustic echo and noise reduction (AENR) often require high memory and computational resources, making them unsuitable for real-time deployment on low-resource platforms such as embedded devices. We propose a low-complexity hybrid approach for joint AENR by employing a single model to suppress both residual echo and noise components. Specifically, we integrate the state-of-the-art (SOTA) ULCNet model, which was originally proposed to achieve ultra-low complexity noise suppression, in a hybrid system and train it for joint AENR. We show that the proposed approach achieves better echo reduction and comparable noise reduction performance with much lower computational complexity and memory requirements than all considered SOTA methods, at the cost of slight degradation in speech quality.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge