A Critical Investigation of Deep Reinforcement Learning for Navigation
Paper and Code
Jan 04, 2019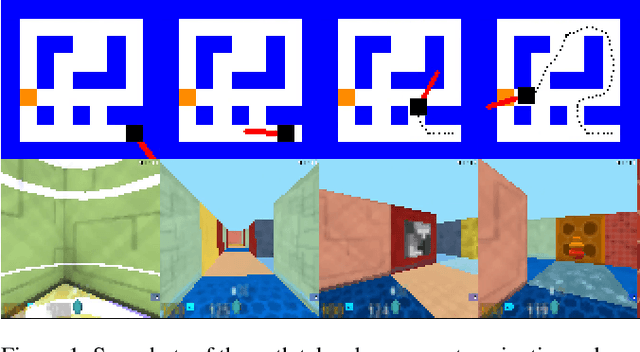


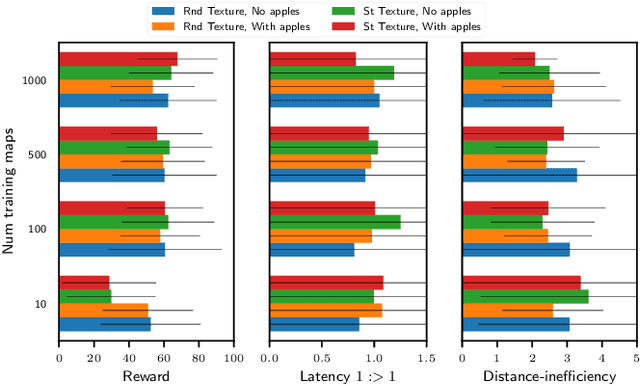
The navigation problem is classically approached in two steps: an exploration step, where map-information about the environment is gathered; and an exploitation step, where this information is used to navigate efficiently. Deep reinforcement learning (DRL) algorithms, alternatively, approach the problem of navigation in an end-to-end fashion. Inspired by the classical approach, we ask whether DRL algorithms are able to inherently explore, gather and exploit map-information over the course of navigation. We build upon Mirowski et al. [2017] work and introduce a systematic suite of experiments that vary three parameters: the agent's starting location, the agent's target location, and the maze structure. We choose evaluation metrics that explicitly measure the algorithm's ability to gather and exploit map-information. Our experiments show that when trained and tested on the same maps, the algorithm successfully gathers and exploits map-information. However, when trained and tested on different sets of maps, the algorithm fails to transfer the ability to gather and exploit map-information to unseen maps. Furthermore, we find that when the goal location is randomized and the map is kept static, the algorithm is able to gather and exploit map-information but the exploitation is far from optimal. We open-source our experimental suite in the hopes that it serves as a framework for the comparison of future algorithms and leads to the discovery of robust alternatives to classical navigation methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge