A Contribution-based Device Selection Scheme in Federated Learning
Paper and Code
Mar 10, 2022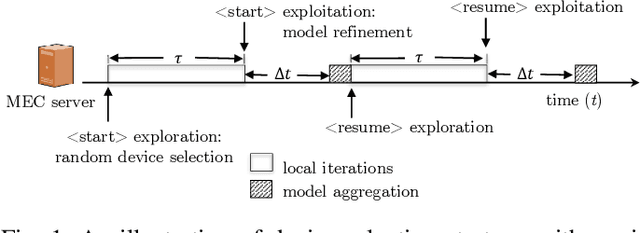


In a Federated Learning (FL) setup, a number of devices contribute to the training of a common model. We present a method for selecting the devices that provide updates in order to achieve improved generalization, fast convergence, and better device-level performance. We formulate a min-max optimization problem and decompose it into a primal-dual setup, where the duality gap is used to quantify the device-level performance. Our strategy combines \emph{exploration} of data freshness through a random device selection with \emph{exploitation} through simplified estimates of device contributions. This improves the performance of the trained model both in terms of generalization and personalization. A modified Truncated Monte-Carlo (TMC) method is applied during the exploitation phase to estimate the device's contribution and lower the communication overhead. The experimental results show that the proposed approach has a competitive performance, with lower communication overhead and competitive personalization performance against the baseline schemes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge