A comparison of visual representations for real-world reinforcement learning in the context of vacuum gripping
Paper and Code
Mar 04, 2025
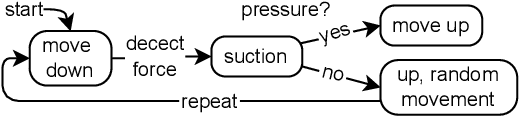


When manipulating objects in the real world, we need reactive feedback policies that take into account sensor information to inform decisions. This study aims to determine how different encoders can be used in a reinforcement learning (RL) framework to interpret the spatial environment in the local surroundings of a robot arm. Our investigation focuses on comparing real-world vision with 3D scene inputs, exploring new architectures in the process. We built on the SERL framework, providing us with a sample efficient and stable RL foundation we could build upon, while keeping training times minimal. The results of this study indicate that spatial information helps to significantly outperform the visual counterpart, tested on a box picking task with a vacuum gripper. The code and videos of the evaluations are available at https://github.com/nisutte/voxel-serl.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge