28 GHz Phased Array-Based Self-Interference Measurements for Millimeter Wave Full-Duplex
Paper and Code
Mar 05, 2022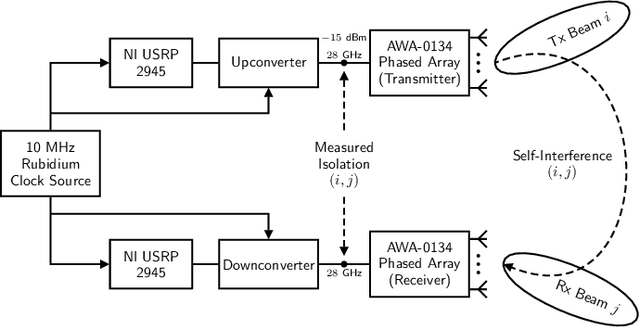


We present measurements of the 28 GHz self-interference channel for full-duplex sectorized multi-panel millimeter wave (mmWave) systems, such as integrated access and backhaul. We measure the isolation between the input of a transmitting phased array panel and the output of a co-located receiving phased array panel, each of which is electronically steered across a number of directions in azimuth and elevation. In total, nearly 6.5 million measurements were taken in an anechoic chamber to densely inspect the directional nature of the coupling between 256-element phased arrays. We observe that highly directional mmWave beams do not necessarily offer widespread high isolation between transmitting and receiving arrays. Rather, our measurements indicate that steering the transmitter or receiver away from the other tends to offer higher isolation but even slight steering changes can lead to drastic variations in isolation. These measurements can be useful references when developing mmWave full-duplex solutions and can motivate a variety of future topics including beam/user selection and beamforming codebook design.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge