2020 U.S. Presidential Election: Analysis of Female and Male Users on Twitter
Paper and Code
Aug 21, 2021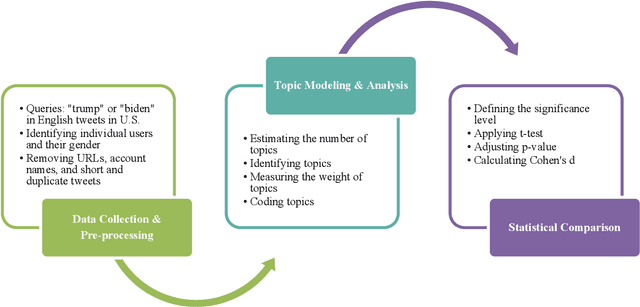
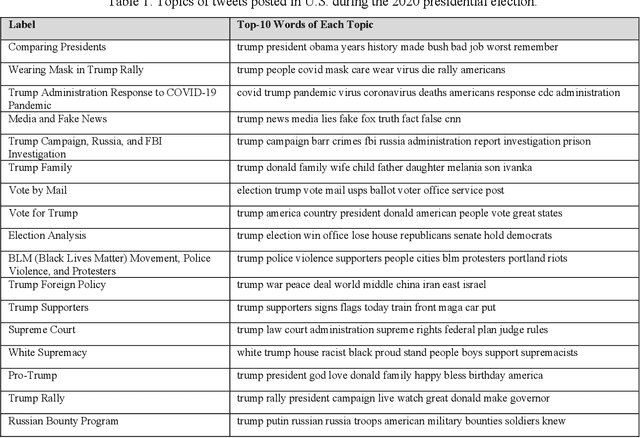
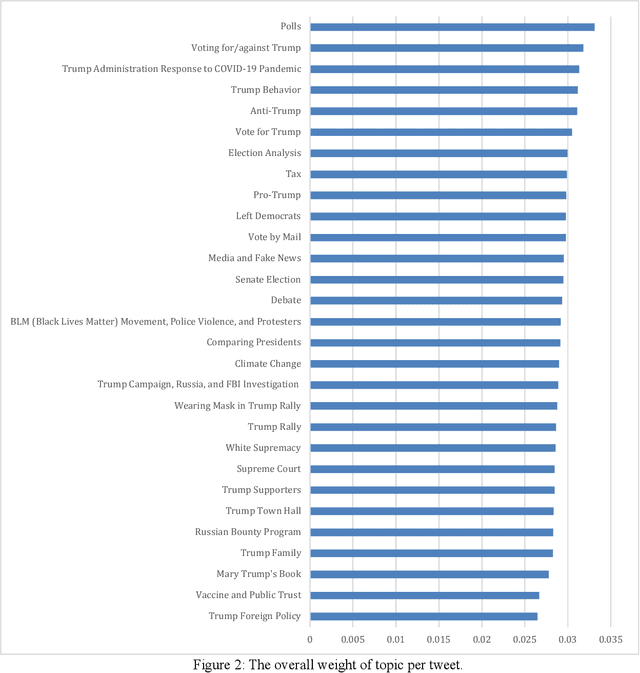
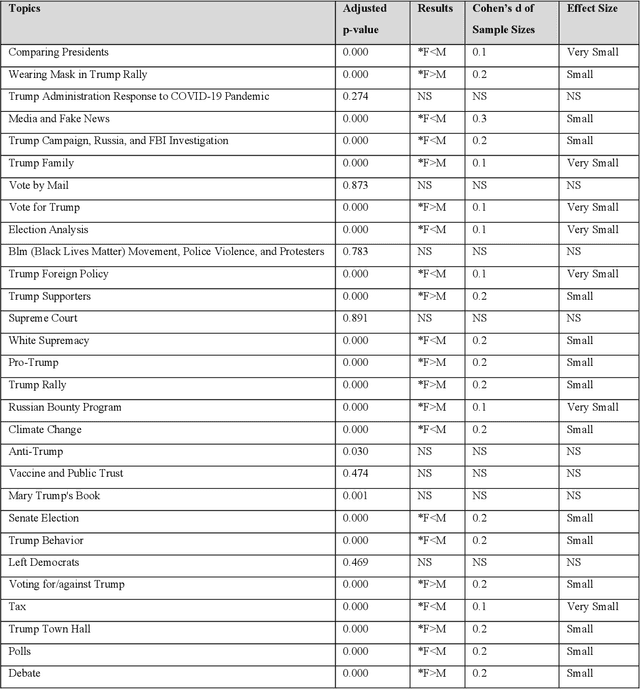
Social media is commonly used by the public during election campaigns to express their opinions regarding different issues. Among various social media channels, Twitter provides an efficient platform for researchers and politicians to explore public opinion regarding a wide range of topics such as economy and foreign policy. Current literature mainly focuses on analyzing the content of tweets without considering the gender of users. This research collects and analyzes a large number of tweets and uses computational, human coding, and statistical analyses to identify topics in more than 300,000 tweets posted during the 2020 U.S. presidential election and to compare female and male users regarding the average weight of the topics. Our findings are based upon a wide range of topics, such as tax, climate change, and the COVID-19 pandemic. Out of the topics, there exists a significant difference between female and male users for more than 70% of topics. Our research approach can inform studies in the areas of informatics, politics, and communication, and it can be used by political campaigns to obtain a gender-based understanding of public opinion.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge