Ziyaur Rahman
Diversity Analysis of Multi-Aperture UWOC System over EGG Channel with Pointing Errors
Dec 19, 2022



Abstract:Single aperture reception for underwater wireless optical communication (UWOC) is insufficient to deal with oceanic turbulence caused by the combined effect of temperature gradient and air bubbles. This paper analyzes the performance of multi-aperture reception for UWOC under channel irradiance fluctuations characterized by the mixture exponential generalized gamma (EGG) distribution. We analyze the system performance by employing both selection combining (SC) and maximum ratio combining (MRC) receivers. In particular, we derive the exact outage probability expression for the SC-based multi-aperture UWOC receiver and obtain an upper bound on the outage probability for the MRC-based multi-aperture UWOC receiver. With the help of the derived results, we analytically obtain the diversity order of the considered multi-aperture UWOC system.
Direct Air-to-Underwater Optical Wireless Communication: Statistical Characterization and Outage Performance
Apr 28, 2022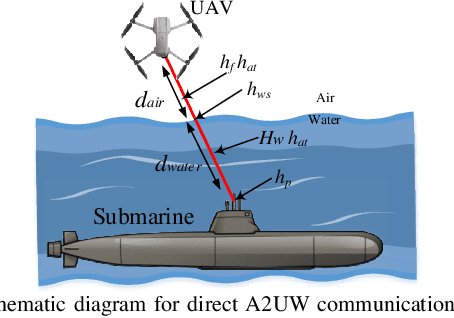
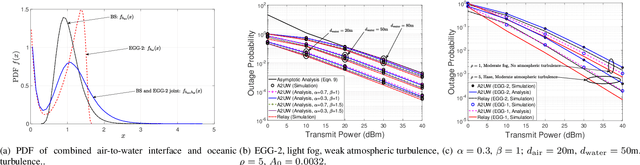
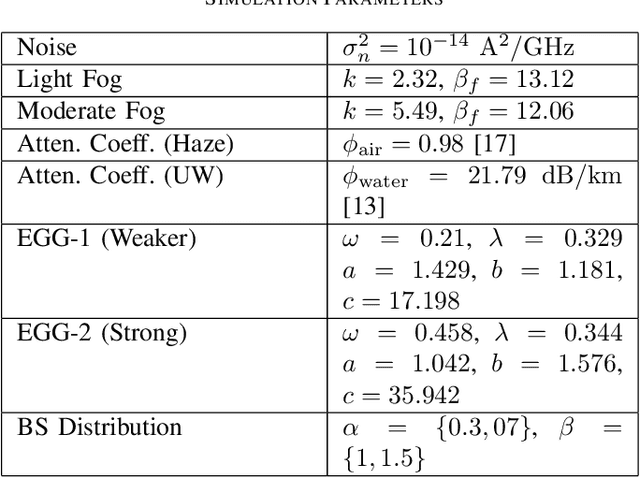
Abstract:In general, a buoy relay is used to connect the underwater communication to the terrestrial network over a radio or optical wireless communication (OWC) link. The use of relay deployment may pose security and deployment issues. This paper investigates the feasibility of direct air-to-underwater (A2UW) communication from an over-the-sea OWC system to an underwater submarine without deploying a relaying node. We analyze the statistical performance of the direct transmission over the combined channel fading effect of atmospheric turbulence, random fog, air-to-water interface, oceanic turbulence, and pointing errors. We develop novel analytical expressions for the probability density function (PDF) and cumulative distribution function (CDF) of the resultant signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) in terms of bivariate Meijer-G and Fox-H functions. We use the derived statistical results to analyze the system performance by providing exact and asymptotic results of the outage probability in terms of system parameters. We use computer simulations to demonstrate the performance of direct A2UW transmissions compared to the relay-assisted system.
Optical Wireless Transmissions over Multi-layer Underwater Channels with Generalized Gamma Fading
Mar 26, 2022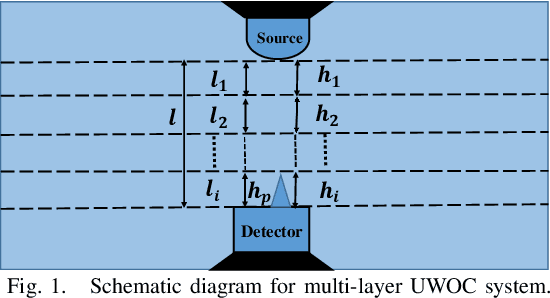
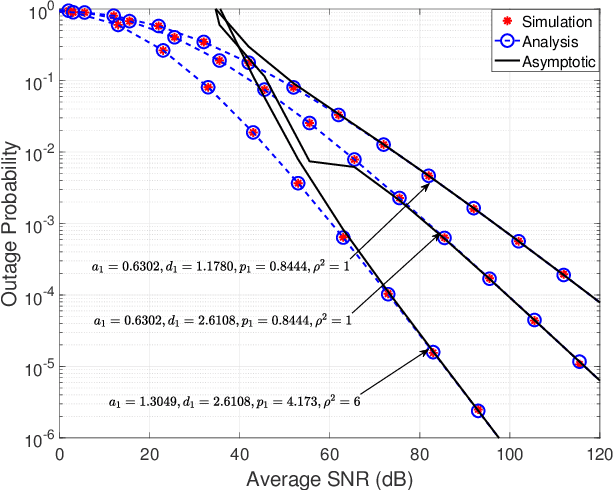
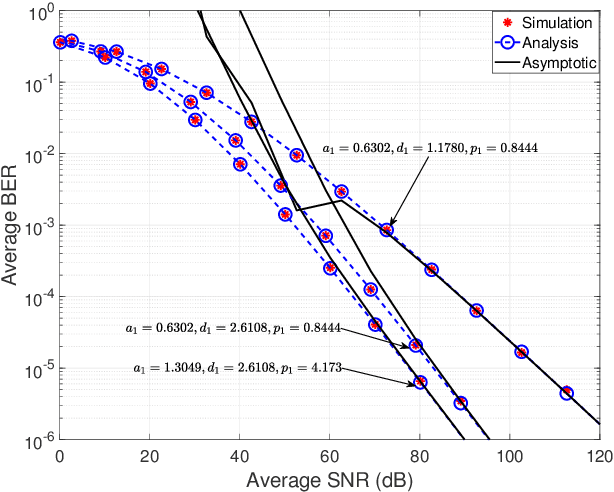
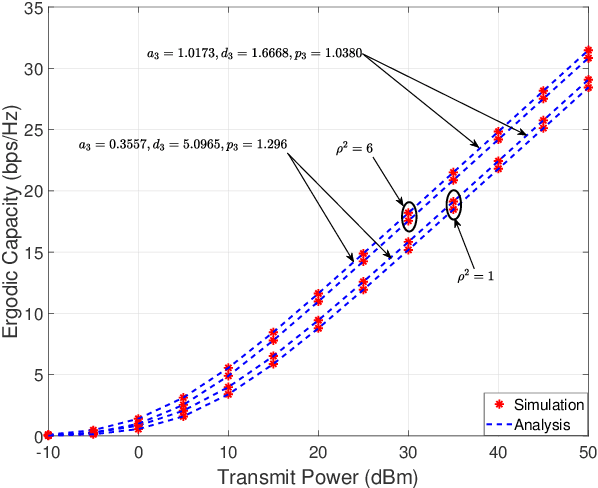
Abstract:Underwater optical communication (UWOC) is a potential solution for broadband connectivity in oceans and seas for underwater applications providing high data rate transmission with low latency and high reliability. Recent measurement campaigns suggest generalized Gamma distribution as a viable model for oceanic turbulence. In this paper, we analyze the performance of a UWOC system by modeling the vertical underwater link as a multi-layer cascaded channel, each distributed according to independent but not identically distributed (i.ni.d.) generalized Gamma random variables and considering the zero bore-sight model for pointing errors. We derive analytical expressions for probability density function (PDF) and cumulative distribution function (CDF) for the signal-to-noise ratios (SNR) of the combined channel and develop performance metrics of the considered UWOC system using outage probability, average bit error rate (BER), and ergodic capacity. We also derive the asymptotic expressions for outage probability and average BER to determine the diversity order of the proposed system for a better insight into the system performance. We use Monte-Carlo simulation results to validate our exact and asymptotic expressions and demonstrate the performance of the considered underwater UWOC system using measurement-based parametric data available for turbulent oceanic channels.
Performance of Dual-Hop Relaying for OWC System Over Foggy Channel with Pointing Errors and Atmospheric Turbulence
May 29, 2021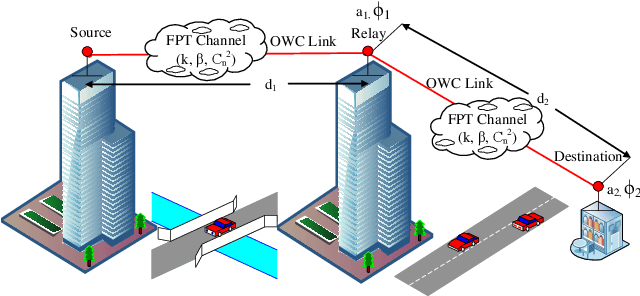
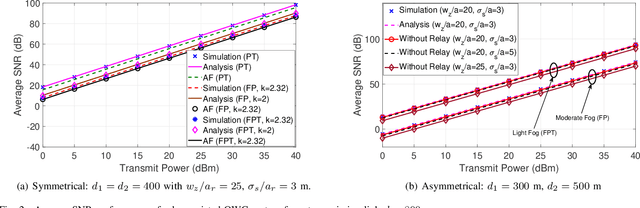
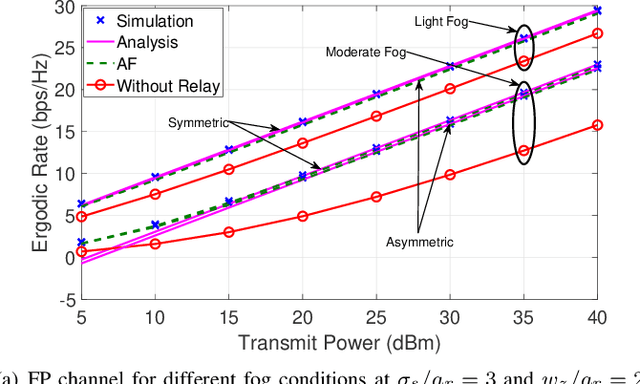
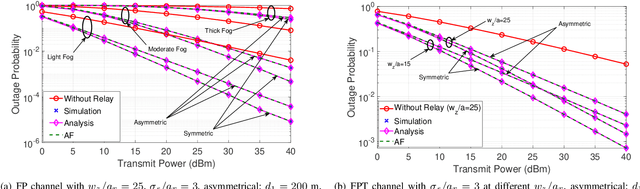
Abstract:Optical wireless communication (OWC) over atmospheric turbulence and pointing errors is a well-studied topic. Still, there is limited research on signal fading due to random fog and pointing errors in outdoor environments. In this paper, we analyze the performance of a decode-and-forward (DF) relaying under the combined effect of random fog, pointing errors, and atmospheric turbulence with a negligible line-of-sight (LOS) direct link. We consider a generalized model for the end-to-end channel with independent and not identically distributed (i.ni.d.) pointing errors, random fog with Gamma distributed attenuation coefficient, asymptotic exponentiated Weibull turbulence, and asymmetrical distance between the source and destination. We derive distribution functions of the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), and then we develop analytical expressions of the outage probability, average SNR, ergodic rate, and average bit error rate (BER) in terms of OWC system parameters. We also develop simplified performance to provide insight on the system behavior analytically under various practically relevant scenarios. We demonstrate the mutual effects of channel impairments and pointing errors on the OWC performance, and show that the relaying system provides significant performance improvement compared with the direct transmissions, especially when pointing errors and fog becomes more pronounced.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge