Direct Air-to-Underwater Optical Wireless Communication: Statistical Characterization and Outage Performance
Paper and Code
Apr 28, 2022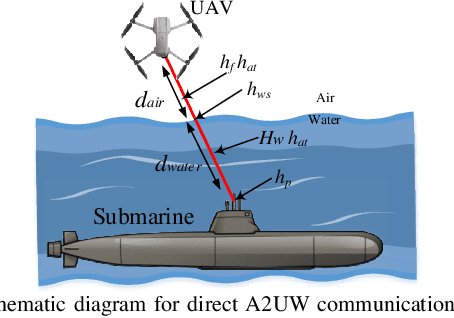
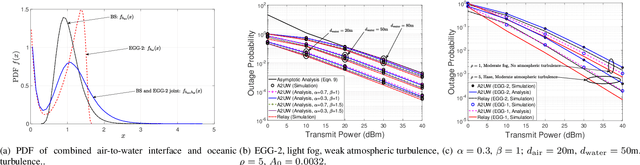
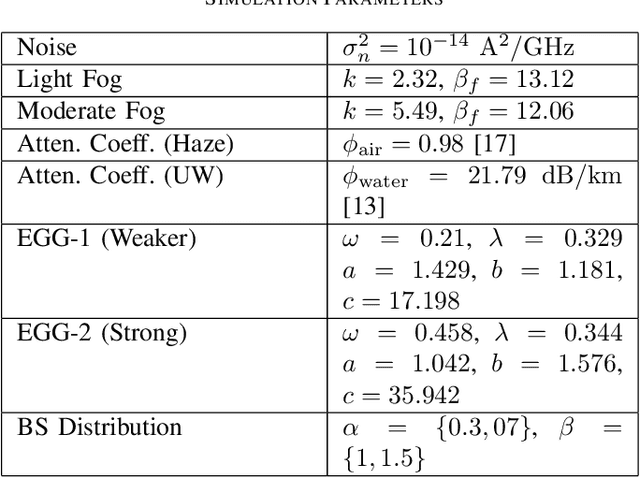
In general, a buoy relay is used to connect the underwater communication to the terrestrial network over a radio or optical wireless communication (OWC) link. The use of relay deployment may pose security and deployment issues. This paper investigates the feasibility of direct air-to-underwater (A2UW) communication from an over-the-sea OWC system to an underwater submarine without deploying a relaying node. We analyze the statistical performance of the direct transmission over the combined channel fading effect of atmospheric turbulence, random fog, air-to-water interface, oceanic turbulence, and pointing errors. We develop novel analytical expressions for the probability density function (PDF) and cumulative distribution function (CDF) of the resultant signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) in terms of bivariate Meijer-G and Fox-H functions. We use the derived statistical results to analyze the system performance by providing exact and asymptotic results of the outage probability in terms of system parameters. We use computer simulations to demonstrate the performance of direct A2UW transmissions compared to the relay-assisted system.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge