Ziqin Chen
Privacy-Preserving Distributed Optimization and Learning
Feb 29, 2024Abstract:Distributed optimization and learning has recently garnered great attention due to its wide applications in sensor networks, smart grids, machine learning, and so forth. Despite rapid development, existing distributed optimization and learning algorithms require each agent to exchange messages with its neighbors, which may expose sensitive information and raise significant privacy concerns. In this survey paper, we overview privacy-preserving distributed optimization and learning methods. We first discuss cryptography, differential privacy, and other techniques that can be used for privacy preservation and indicate their pros and cons for privacy protection in distributed optimization and learning. We believe that among these approaches, differential privacy is most promising due to its low computational and communication complexities, which are extremely appealing for modern learning based applications with high dimensions of optimization variables. We then introduce several differential-privacy algorithms that can simultaneously ensure privacy and optimization accuracy. Moreover, we provide example applications in several machine learning problems to confirm the real-world effectiveness of these algorithms. Finally, we highlight some challenges in this research domain and discuss future directions.
Locally Differentially Private Gradient Tracking for Distributed Online Learning over Directed Graphs
Oct 29, 2023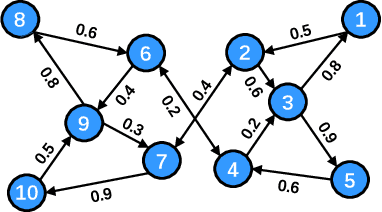
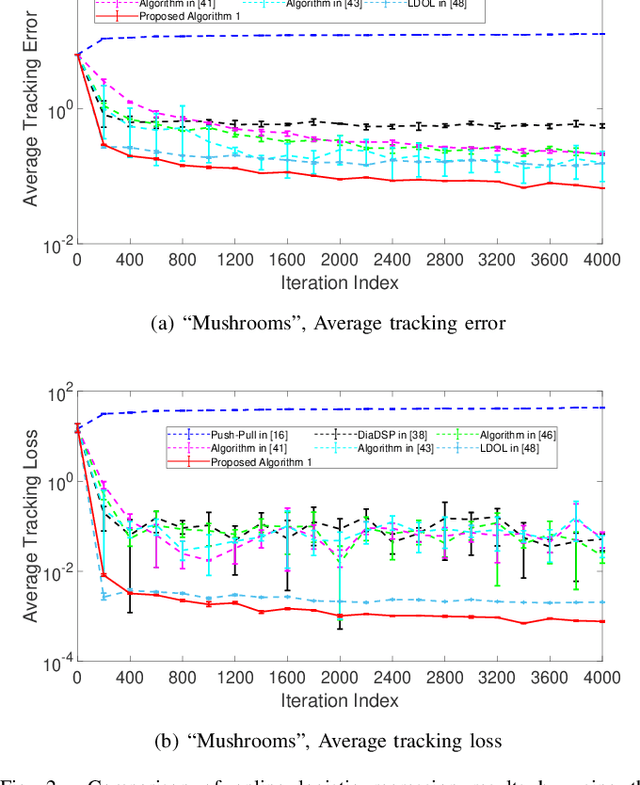
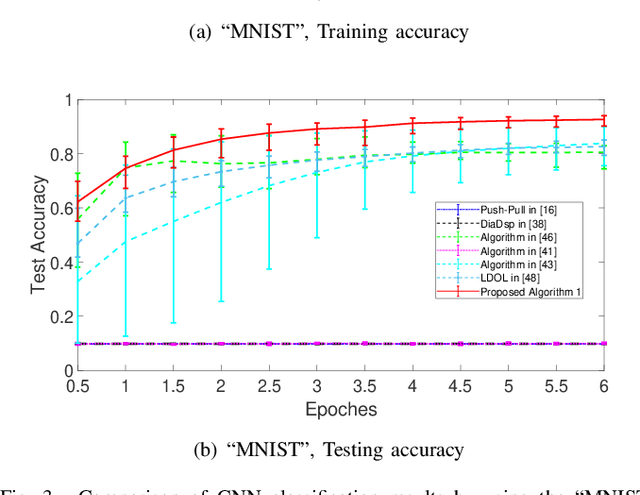
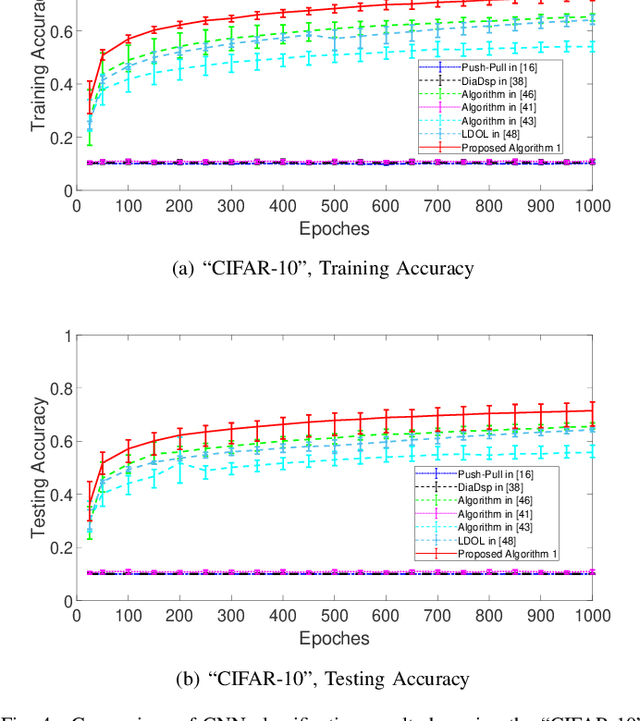
Abstract:Distributed online learning has been proven extremely effective in solving large-scale machine learning problems over streaming data. However, information sharing between learners in distributed learning also raises concerns about the potential leakage of individual learners' sensitive data. To mitigate this risk, differential privacy, which is widely regarded as the "gold standard" for privacy protection, has been widely employed in many existing results on distributed online learning. However, these results often face a fundamental tradeoff between learning accuracy and privacy. In this paper, we propose a locally differentially private gradient tracking based distributed online learning algorithm that successfully circumvents this tradeoff. We prove that the proposed algorithm converges in mean square to the exact optimal solution while ensuring rigorous local differential privacy, with the cumulative privacy budget guaranteed to be finite even when the number of iterations tends to infinity. The algorithm is applicable even when the communication graph among learners is directed. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first result that simultaneously ensures learning accuracy and rigorous local differential privacy in distributed online learning over directed graphs. We evaluate our algorithm's performance by using multiple benchmark machine-learning applications, including logistic regression of the "Mushrooms" dataset and CNN-based image classification of the "MNIST" and "CIFAR-10" datasets, respectively. The experimental results confirm that the proposed algorithm outperforms existing counterparts in both training and testing accuracies.
Locally Differentially Private Distributed Online Learning with Guaranteed Optimality
Jun 25, 2023Abstract:Distributed online learning is gaining increased traction due to its unique ability to process large-scale datasets and streaming data. To address the growing public awareness and concern on privacy protection, plenty of private distributed online learning algorithms have been proposed, mostly based on differential privacy which has emerged as the ``gold standard" for privacy protection. However, these algorithms often face the dilemma of trading learning accuracy for privacy. By exploiting the unique characteristics of online learning, this paper proposes an approach that tackles the dilemma and ensures both differential privacy and learning accuracy in distributed online learning. More specifically, while ensuring a diminishing expected instantaneous regret, the approach can simultaneously ensure a finite cumulative privacy budget, even on the infinite time horizon. To cater for the fully distributed setting, we adopt the local differential-privacy framework which avoids the reliance on a trusted data curator, and hence, provides stronger protection than the classic ``centralized" (global) differential privacy. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first algorithm that successfully ensures both rigorous local differential privacy and learning accuracy. The effectiveness of the proposed algorithm is evaluated using machine learning tasks, including logistic regression on the ``Mushrooms" and ``Covtype" datasets and CNN based image classification on the ``MNIST" and ``CIFAR-10" datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge