Ziman Zhuang
Children's Acquisition of Tail-recursion Sequences: A Review of Locative Recursion and Possessive Recursion as Examples
Dec 28, 2024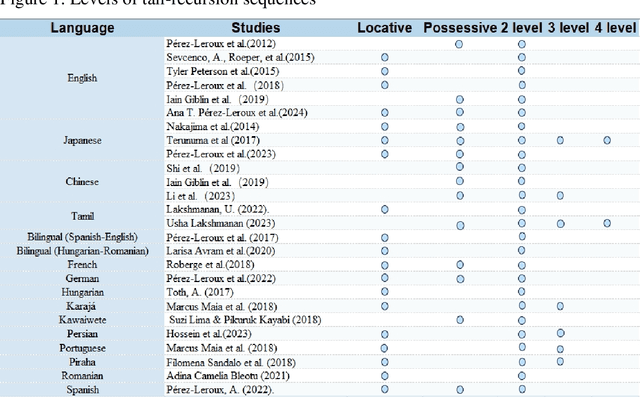
Abstract:Recursion is the nature of human natural language. Since Chomsky proposed generative grammar, many scholars have studied recursion either theoretically or empirically. However, by observing children's acquisition of tail recursion sequences, we can verify the nativism of language supported by universal grammar and reveal the cognitive mechanism of human brain. To date, our understanding of children's acquisition path of recursion and influencing factors still remain controversial. This systematic review summarizes the research of tail recursive sequence by taking possessive recursion and locative recursion as examples, focusing on the experimental methods, acquisition paths, and influencing factors of tail recursive sequence. The current behavioural experiments reveal that, the debate about children's performance revolves around: 1) Gradual acquisition or synchronous acquisition. 2) symmetry or asymmetry between the acquisition of locative recursion sequences and possessive recursion sequences. We presume that children can acquire recursion quickly in a short period of time thanks to the language acquisition device, though there are also scholars who believe that a third factor also plays a role.
Grammaticality illusion or ambiguous interpretation? Event-related potentials reveal the nature of the missing-NP effect in Mandarin centre-embedded structures
Feb 17, 2024Abstract:In several languages, omitting a verb phrase (VP) in double centre-embedded structures creates a grammaticality illusion. Similar illusion also exhibited in Mandarin missing-NP double centre-embedded structures. However, there is no consensus on its very nature. Instead of treating it as grammaticality illusion, we argue that ambiguous interpretations of verbs can best account for this phenomenon in Mandarin. To further support this hypothesis, we conducted two electroencephalography (EEG) experiments on quasi double centre-embedded structures whose complexity is reduced by placing the self-embedding relative clauses into the sentence's subject position. Experiment 1 showed that similar phenomenon even exhibited in this structure, evidenced by an absence of P600 effect and a presence of N400 effect. In Experiment 2, providing semantic cues to reduce ambiguity dispelled this illusion, as evidenced by a P600 effect. We interpret the results under garden-path theory and propose that word-order difference may account for this cross-linguistic variation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge