Zhiyan Zhong
Spatio-Temporal Feedback Control of Small Target Motion Detection Visual System
Nov 18, 2022



Abstract:Feedback is crucial to motion perception in animals' visual systems where its spatial and temporal dynamics are often shaped by movement patterns of surrounding environments. However, such spatio-temporal feedback has not been deeply explored in designing neural networks to detect small moving targets that cover only one or a few pixels in image while presenting extremely limited visual features. In this paper, we address small target motion detection problem by developing a visual system with spatio-temporal feedback loop, and further reveal its important roles in suppressing false positive background movement while enhancing network responses to small targets. Specifically, the proposed visual system is composed of two complementary subnetworks. The first subnetwork is designed to extract spatial and temporal motion patterns of cluttered backgrounds by neuronal ensemble coding. The second subnetwork is developed to capture small target motion information and integrate the spatio-temporal feedback signal from the first subnetwork to inhibit background false positives. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed spatio-temporal feedback visual system is more competitive than existing methods in discriminating small moving targets from complex dynamic environment.
Analyzing Folktales of Different Regions Using Topic Modeling and Clustering
Jun 09, 2022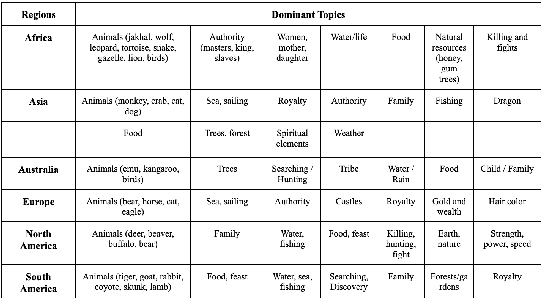
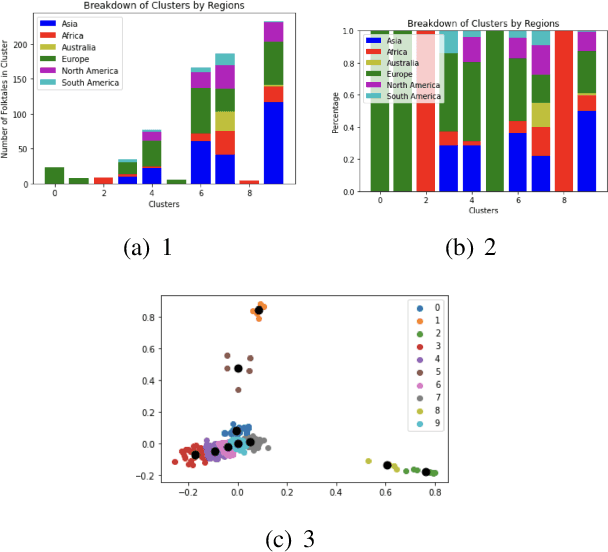
Abstract:This paper employs two major natural language processing techniques, topic modeling and clustering, to find patterns in folktales and reveal cultural relationships between regions. In particular, we used Latent Dirichlet Allocation and BERTopic to extract the recurring elements as well as K-means clustering to group folktales. Our paper tries to answer the question what are the similarities and differences between folktales, and what do they say about culture. Here we show that the common trends between folktales are family, food, traditional gender roles, mythological figures, and animals. Also, folktales topics differ based on geographical location with folktales found in different regions having different animals and environment. We were not surprised to find that religious figures and animals are some of the common topics in all cultures. However, we were surprised that European and Asian folktales were often paired together. Our results demonstrate the prevalence of certain elements in cultures across the world. We anticipate our work to be a resource to future research of folktales and an example of using natural language processing to analyze documents in specific domains. Furthermore, since we only analyzed the documents based on their topics, more work could be done in analyzing the structure, sentiment, and the characters of these folktales.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge