Yuping Fan
DRAS-CQSim: A Reinforcement Learning based Framework for HPC Cluster Scheduling
May 16, 2021


Abstract:For decades, system administrators have been striving to design and tune cluster scheduling policies to improve the performance of high performance computing (HPC) systems. However, the increasingly complex HPC systems combined with highly diverse workloads make such manual process challenging, time-consuming, and error-prone. We present a reinforcement learning based HPC scheduling framework named DRAS-CQSim to automatically learn optimal scheduling policy. DRAS-CQSim encapsulates simulation environments, agents, hyperparameter tuning options, and different reinforcement learning algorithms, which allows the system administrators to quickly obtain customized scheduling policies.
Deep Reinforcement Agent for Scheduling in HPC
Feb 11, 2021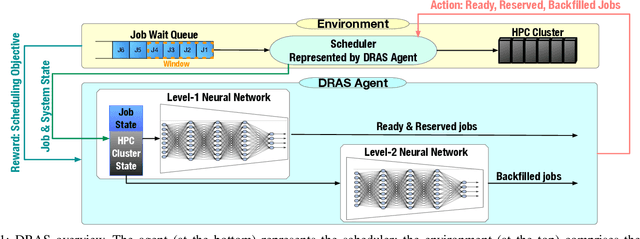



Abstract:Cluster scheduler is crucial in high-performance computing (HPC). It determines when and which user jobs should be allocated to available system resources. Existing cluster scheduling heuristics are developed by human experts based on their experience with specific HPC systems and workloads. However, the increasing complexity of computing systems and the highly dynamic nature of application workloads have placed tremendous burden on manually designed and tuned scheduling heuristics. More aggressive optimization and automation are needed for cluster scheduling in HPC. In this work, we present an automated HPC scheduling agent named DRAS (Deep Reinforcement Agent for Scheduling) by leveraging deep reinforcement learning. DRAS is built on a novel, hierarchical neural network incorporating special HPC scheduling features such as resource reservation and backfilling. A unique training strategy is presented to enable DRAS to rapidly learn the target environment. Once being provided a specific scheduling objective given by system manager, DRAS automatically learns to improve its policy through interaction with the scheduling environment and dynamically adjusts its policy as workload changes. The experiments with different production workloads demonstrate that DRAS outperforms the existing heuristic and optimization approaches by up to 45%.
* Accepted by IPDPS 2021
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge