Yung Jer Wong
Local Statistics for Generative Image Detection
Oct 25, 2023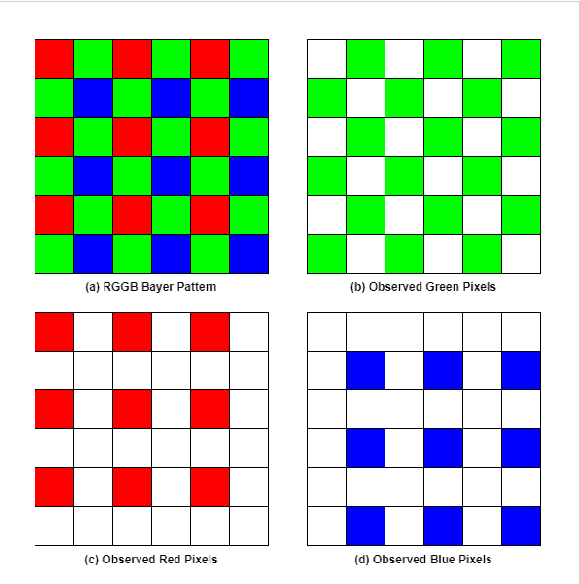
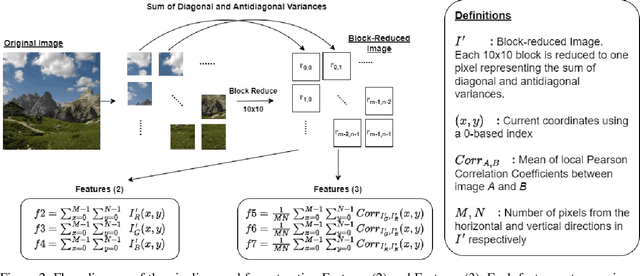
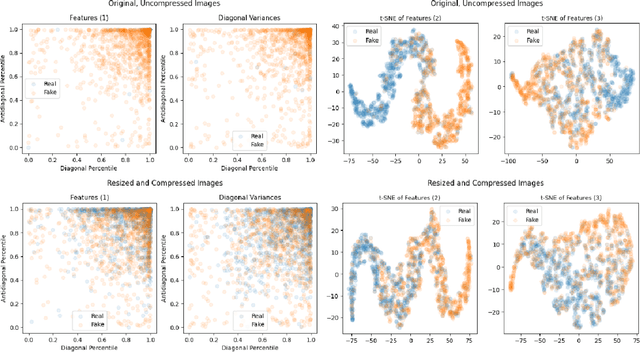
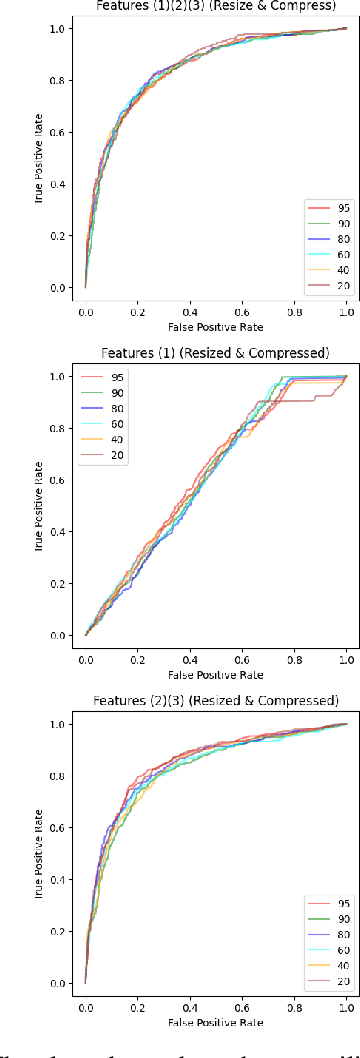
Abstract:Diffusion models (DMs) are generative models that learn to synthesize images from Gaussian noise. DMs can be trained to do a variety of tasks such as image generation and image super-resolution. Researchers have made significant improvement in the capability of synthesizing photorealistic images in the past few years. These successes also hasten the need to address the potential misuse of synthesized images. In this paper, we highlight the effectiveness of computing local statistics, as opposed to global statistics, in distinguishing digital camera images from DM-generated images. We hypothesized that local statistics should be used to address the spatial non-stationarity problem in images. We show that our approach produced promising results and it is also robust to various perturbations such as image resizing and JPEG compression.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge