Yufan Xia
A Machine Learning Approach Towards Runtime Optimisation of Matrix Multiplication
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:The GEneral Matrix Multiplication (GEMM) is one of the essential algorithms in scientific computing. Single-thread GEMM implementations are well-optimised with techniques like blocking and autotuning. However, due to the complexity of modern multi-core shared memory systems, it is challenging to determine the number of threads that minimises the multi-thread GEMM runtime. We present a proof-of-concept approach to building an Architecture and Data-Structure Aware Linear Algebra (ADSALA) software library that uses machine learning to optimise the runtime performance of BLAS routines. More specifically, our method uses a machine learning model on-the-fly to automatically select the optimal number of threads for a given GEMM task based on the collected training data. Test results on two different HPC node architectures, one based on a two-socket Intel Cascade Lake and the other on a two-socket AMD Zen 3, revealed a 25 to 40 per cent speedup compared to traditional GEMM implementations in BLAS when using GEMM of memory usage within 100 MB.
The Dissipation Theory of Aging: A Quantitative Analysis Using a Cellular Aging Map
Apr 17, 2025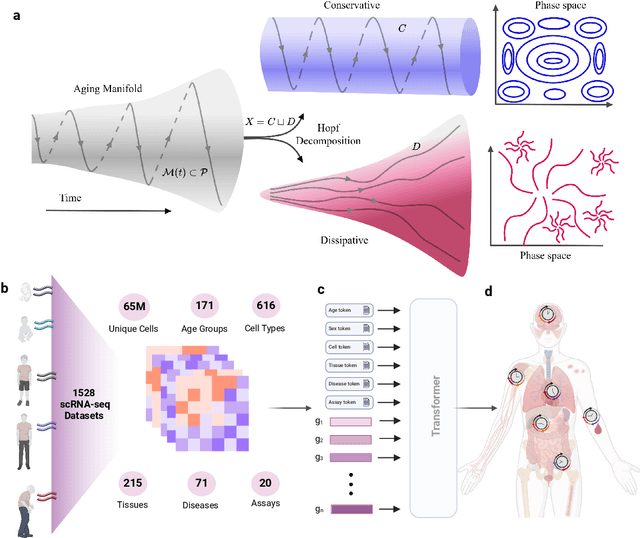
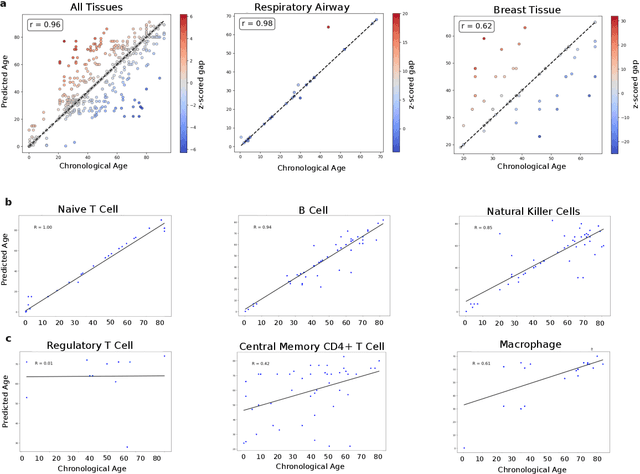
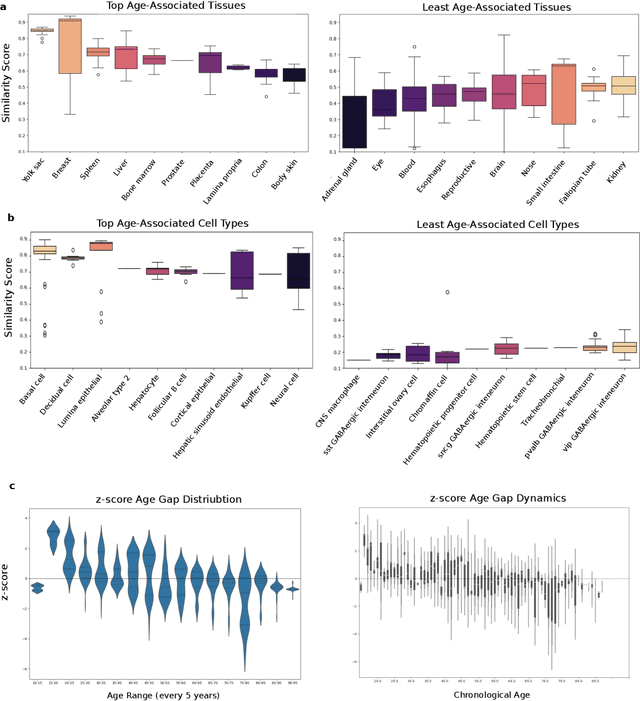
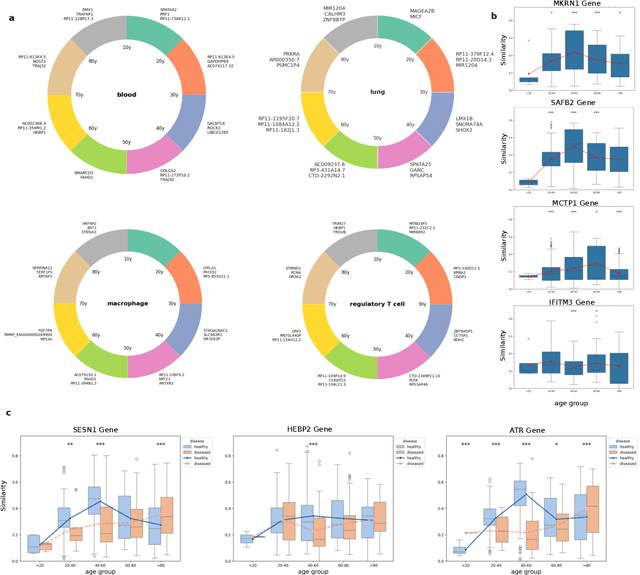
Abstract:We propose a new theory for aging based on dynamical systems and provide a data-driven computational method to quantify the changes at the cellular level. We use ergodic theory to decompose the dynamics of changes during aging and show that aging is fundamentally a dissipative process within biological systems, akin to dynamical systems where dissipation occurs due to non-conservative forces. To quantify the dissipation dynamics, we employ a transformer-based machine learning algorithm to analyze gene expression data, incorporating age as a token to assess how age-related dissipation is reflected in the embedding space. By evaluating the dynamics of gene and age embeddings, we provide a cellular aging map (CAM) and identify patterns indicative of divergence in gene embedding space, nonlinear transitions, and entropy variations during aging for various tissues and cell types. Our results provide a novel perspective on aging as a dissipative process and introduce a computational framework that enables measuring age-related changes with molecular resolution.
Cellular Development Follows the Path of Minimum Action
Apr 10, 2025Abstract:Cellular development follows a stochastic yet rule-governed trajectory, though the underlying principles remain elusive. Here, we propose that cellular development follows paths of least action, aligning with foundational physical laws that govern dynamic systems across nature. We introduce a computational framework that takes advantage of the deep connection between the principle of least action and maximum entropy to model developmental processes using Transformers architecture. This approach enables precise quantification of entropy production, information flow curvature, and local irreversibility for developmental asymmetry in single-cell RNA sequence data. Within this unified framework, we provide interpretable metrics: entropy to capture exploration-exploitation trade-offs, curvature to assess plasticity-elasticity dynamics, and entropy production to characterize dedifferentiation and transdifferentiation. We validate our method across both single-cell and embryonic development datasets, demonstrating its ability to reveal hidden thermodynamic and informational constraints shaping cellular fate decisions.
Machine-Learning-Driven Runtime Optimization of BLAS Level 3 on Modern Multi-Core Systems
Jun 28, 2024Abstract:BLAS Level 3 operations are essential for scientific computing, but finding the optimal number of threads for multi-threaded implementations on modern multi-core systems is challenging. We present an extension to the Architecture and Data-Structure Aware Linear Algebra (ADSALA) library that uses machine learning to optimize the runtime of all BLAS Level 3 operations. Our method predicts the best number of threads for each operation based on the matrix dimensions and the system architecture. We test our method on two HPC platforms with Intel and AMD processors, using MKL and BLIS as baseline BLAS implementations. We achieve speedups of 1.5 to 3.0 for all operations, compared to using the maximum number of threads. We also analyze the runtime patterns of different BLAS operations and explain the sources of speedup. Our work shows the effectiveness and generality of the ADSALA approach for optimizing BLAS routines on modern multi-core systems.
* Multi-Thread, Matrix Multiplication, Optimization, BLAS, Machine Learning
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge