Yuchen Lian
Simulating the Emergence of Differential Case Marking with Communicating Neural-Network Agents
Feb 06, 2025

Abstract:Differential Case Marking (DCM) refers to the phenomenon where grammatical case marking is applied selectively based on semantic, pragmatic, or other factors. The emergence of DCM has been studied in artificial language learning experiments with human participants, which were specifically aimed at disentangling the effects of learning from those of communication (Smith & Culbertson, 2020). Multi-agent reinforcement learning frameworks based on neural networks have gained significant interest to simulate the emergence of human-like linguistic phenomena. In this study, we employ such a framework in which agents first acquire an artificial language before engaging in communicative interactions, enabling direct comparisons to human result. Using a very generic communication optimization algorithm and neural-network learners that have no prior experience with language or semantic preferences, our results demonstrate that learning alone does not lead to DCM, but when agents communicate, differential use of markers arises. This supports Smith and Culbertson (2020)'s findings that highlight the critical role of communication in shaping DCM and showcases the potential of neural-agent models to complement experimental research on language evolution.
NeLLCom-X: A Comprehensive Neural-Agent Framework to Simulate Language Learning and Group Communication
Jul 19, 2024Abstract:Recent advances in computational linguistics include simulating the emergence of human-like languages with interacting neural network agents, starting from sets of random symbols. The recently introduced NeLLCom framework (Lian et al., 2023) allows agents to first learn an artificial language and then use it to communicate, with the aim of studying the emergence of specific linguistics properties. We extend this framework (NeLLCom-X) by introducing more realistic role-alternating agents and group communication in order to investigate the interplay between language learnability, communication pressures, and group size effects. We validate NeLLCom-X by replicating key findings from prior research simulating the emergence of a word-order/case-marking trade-off. Next, we investigate how interaction affects linguistic convergence and emergence of the trade-off. The novel framework facilitates future simulations of diverse linguistic aspects, emphasizing the importance of interaction and group dynamics in language evolution.
Communication Drives the Emergence of Language Universals in Neural Agents: Evidence from the Word-order/Case-marking Trade-off
Jan 30, 2023Abstract:Artificial learners often behave differently from human learners in the context of neural agent-based simulations of language emergence and change. The lack of appropriate cognitive biases in these learners is one of the prevailing explanations. However, it has also been proposed that more naturalistic settings of language learning and use could lead to more human-like results. In this work, we investigate the latter account focusing on the word-order/case-marking trade-off, a widely attested language universal which has proven particularly difficult to simulate. We propose a new Neural-agent Language Learning and Communication framework (NeLLCom) where pairs of speaking and listening agents first learn a given miniature language through supervised learning, and then optimize it for communication via reinforcement learning. Following closely the setup of earlier human experiments, we succeed in replicating the trade-off with the new framework without hard-coding any learning bias in the agents. We see this as an essential step towards the investigation of language universals with neural learners.
The Effect of Efficient Messaging and Input Variability on Neural-Agent Iterated Language Learning
Apr 15, 2021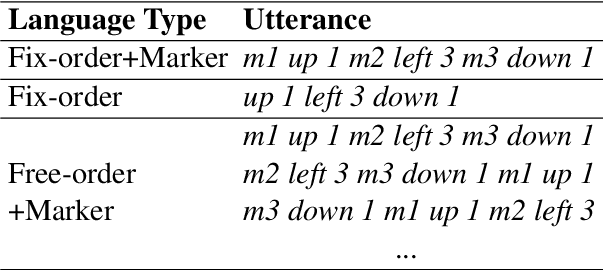

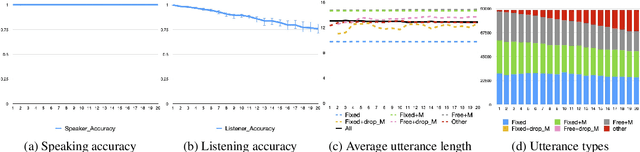

Abstract:Natural languages commonly display a trade-off among different strategies to convey constituent roles. A similar trade-off, however, has not been observed in recent simulations of iterated language learning with neural network based agents (Chaabouni et al., 2019b). In this work, we re-evaluate this result in the light of two important factors, namely: the lack of effort-based pressure in the agents and the lack of variability in the initial input language.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge