Yu Song Meng
Analyzing Solar Irradiance Variation From GPS and Cameras
Apr 19, 2018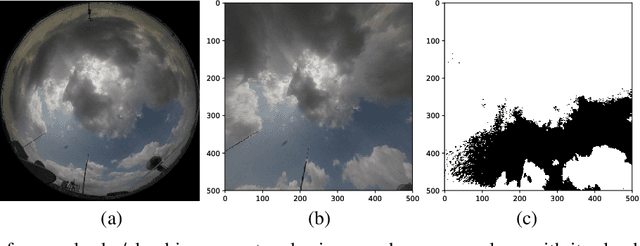
Abstract:The total amount of solar irradiance falling on the earth's surface is an important area of study amongst the photo-voltaic (PV) engineers and remote sensing analysts. The received solar irradiance impacts the total amount of generated solar energy. However, this generation is often hindered by the high degree of solar irradiance variability. In this paper, we study the main factors behind such variability with the assistance of Global Positioning System (GPS) and ground-based, high-resolution sky cameras. This analysis will also be helpful for understanding cloud phenomenon and other events in the earth's atmosphere.
Correlating Satellite Cloud Cover with Sky Cameras
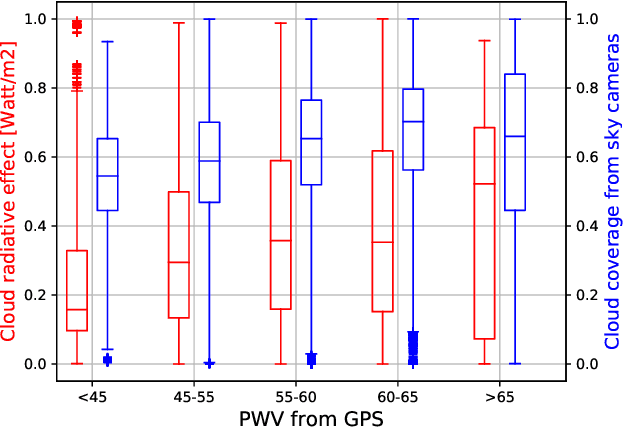
Aug 24, 2017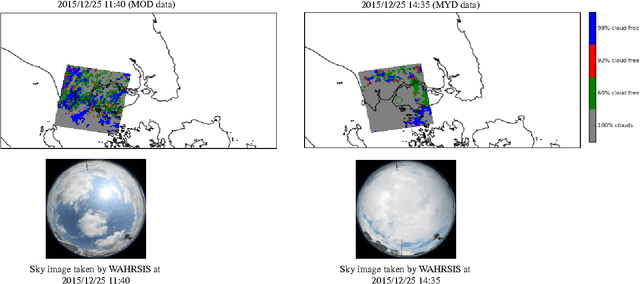
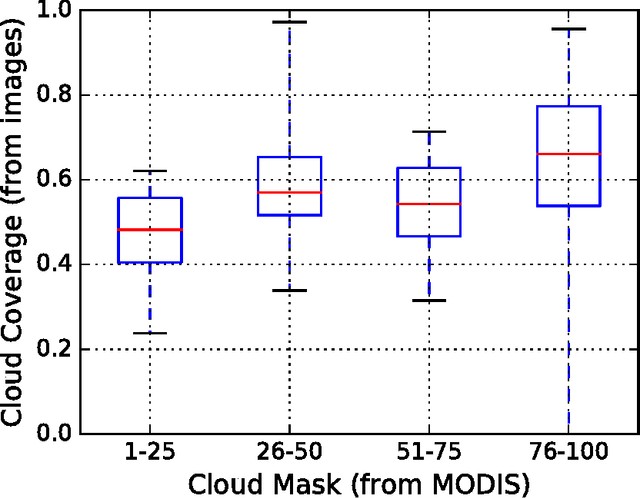
Abstract:The role of clouds is manifold in understanding the various events in the atmosphere, and also in studying the radiative balance of the earth. The conventional manner of such cloud analysis is performed mainly via satellite images. However, because of its low temporal- and spatial- resolutions, ground-based sky cameras are now getting popular. In this paper, we study the relation between the cloud cover obtained from MODIS images, with the coverage obtained from ground-based sky cameras. This will help us to better understand cloud formation in the atmosphere - both from satellite images and ground-based observations.
Analyzing Cloud Optical Properties Using Sky Cameras
Aug 24, 2017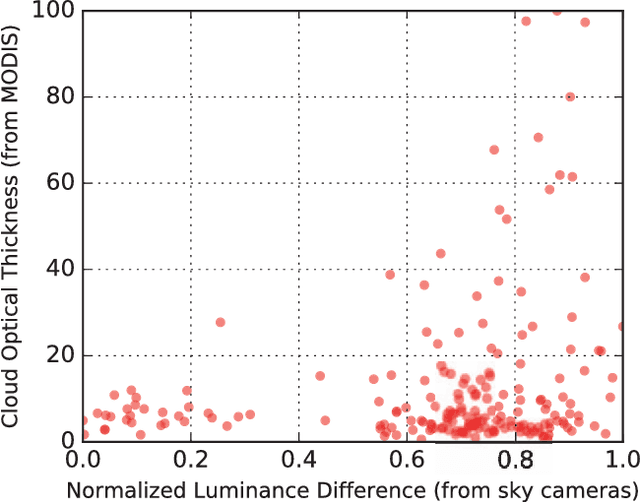
Abstract:Clouds play a significant role in the fluctuation of solar radiation received by the earth's surface. It is important to study the various cloud properties, as it impacts the total solar irradiance falling on the earth's surface. One of such important optical properties of the cloud is the Cloud Optical Thickness (COT). It is defined with the amount of light that can pass through the clouds. The COT values are generally obtained from satellite images. However, satellite images have a low temporal- and spatial- resolutions; and are not suitable for study in applications as solar energy generation and forecasting. Therefore, ground-based sky cameras are now getting popular in such fields. In this paper, we analyze the cloud optical thickness value, from the ground-based sky cameras, and provide future research directions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge