Yohanes Khosiawan
Indoor UAV scheduling with Restful Task Assignment Algorithm
Jun 29, 2017

Abstract:Research in UAV scheduling has obtained an emerging interest from scientists in the optimization field. When the scheduling itself has established a strong root since the 19th century, works on UAV scheduling in indoor environment has come forth in the latest decade. Several works on scheduling UAV operations in indoor (two and three dimensional) and outdoor environments are reported. In this paper, a further study on UAV scheduling in three dimensional indoor environment is investigated. Dealing with indoor environment\textemdash where humans, UAVs, and other elements or infrastructures are likely to coexist in the same space\textemdash draws attention towards the safety of the operations. In relation to the battery level, a preserved battery level leads to safer operations, promoting the UAV to have a decent remaining power level. A methodology which consists of a heuristic approach based on Restful Task Assignment Algorithm, incorporated with Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm, is proposed. The motivation is to preserve the battery level throughout the operations, which promotes less possibility in having failed UAVs on duty. This methodology is tested with 54 benchmark datasets stressing on 4 different aspects: geographical distance, number of tasks, number of predecessors, and slack time. The test results and their characteristics in regard to the proposed methodology are discussed and presented.
Task scheduling system for UAV operations in indoor environment
Apr 21, 2016

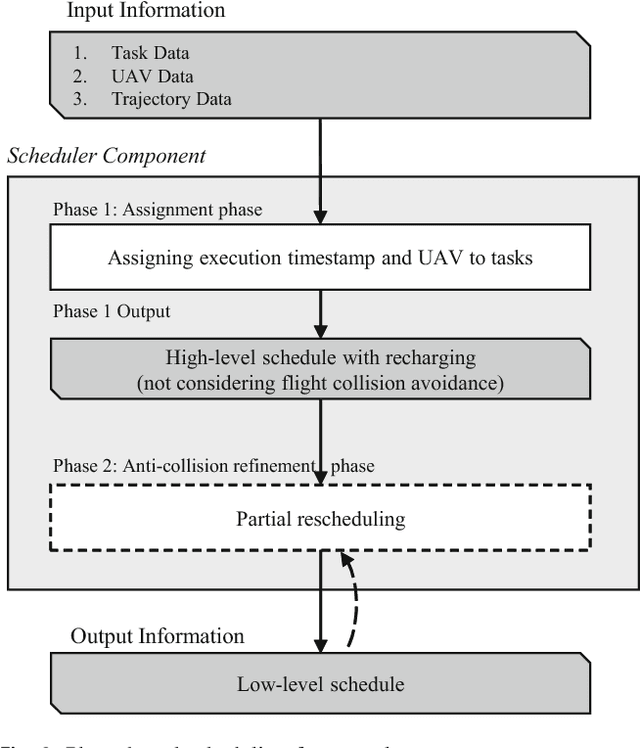

Abstract:Application of UAV in indoor environment is emerging nowadays due to the advancements in technology. UAV brings more space-flexibility in an occupied or hardly-accessible indoor environment, e.g., shop floor of manufacturing industry, greenhouse, nuclear powerplant. UAV helps in creating an autonomous manufacturing system by executing tasks with less human intervention in time-efficient manner. Consequently, a scheduler is one essential component to be focused on; yet the number of reported studies on UAV scheduling has been minimal. This work proposes a methodology with a heuristic (based on Earliest Available Time algorithm) which assigns tasks to UAVs with an objective of minimizing the makespan. In addition, a quick response towards uncertain events and a quick creation of new high-quality feasible schedule are needed. Hence, the proposed heuristic is incorporated with Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) algorithm to find a quick near optimal schedule. This proposed methodology is implemented into a scheduler and tested on a few scales of datasets generated based on a real flight demonstration. Performance evaluation of scheduler is discussed in detail and the best solution obtained from a selected set of parameters is reported.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge