Yicheng Sun
Constructing Cloze Questions Generatively
Oct 05, 2024Abstract:We present a generative method called CQG for constructing cloze questions from a given article using neural networks and WordNet, with an emphasis on generating multigram distractors. Built on sense disambiguation, text-to-text transformation, WordNet's synset taxonomies and lexical labels, CQG selects an answer key for a given sentence, segments it into a sequence of instances, generates instance-level distractor candidates (IDCs) using a transformer and sibling synsets.It then removes inappropriate IDCs, ranks the remaining IDCs based on contextual embedding similarities, as well as synset and lexical relatedness, forms distractor candidates by combinatorially replacing instances with the corresponding top-ranked IDCs, and checks if they are legitimate phrases. Finally, it selects top-ranked distractor candidates based on contextual semantic similarities to the answer key. Experiments show that this method significantly outperforms SOTA results. Human judges also confirm the high qualities of the generated distractors.
* 8 pages, 5 figures,5 tables, 2023 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN)
Generating Adequate Distractors for Multiple-Choice Questions
Oct 23, 2020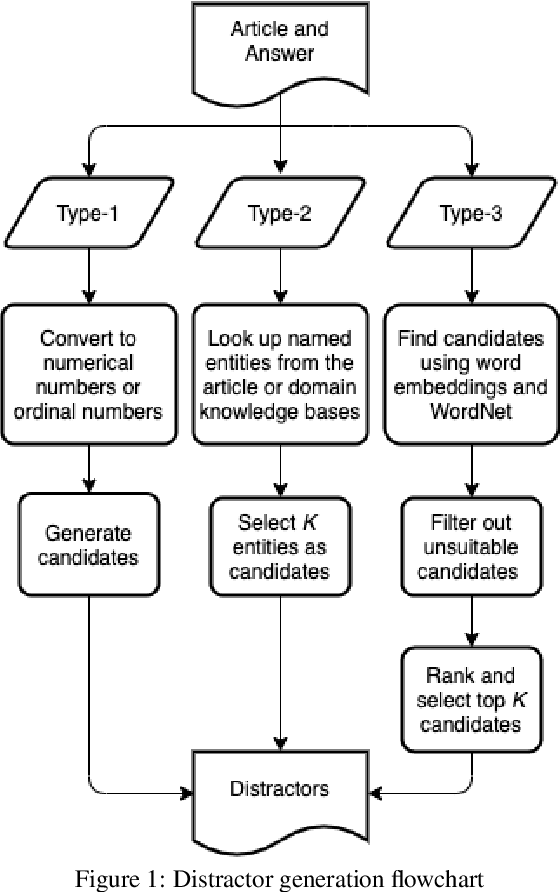
Abstract:This paper presents a novel approach to automatic generation of adequate distractors for a given question-answer pair (QAP) generated from a given article to form an adequate multiple-choice question (MCQ). Our method is a combination of part-of-speech tagging, named-entity tagging, semantic-role labeling, regular expressions, domain knowledge bases, word embeddings, word edit distance, WordNet, and other algorithms. We use the US SAT (Scholastic Assessment Test) practice reading tests as a dataset to produce QAPs and generate three distractors for each QAP to form an MCQ. We show that, via experiments and evaluations by human judges, each MCQ has at least one adequate distractor and 84\% of MCQs have three adequate distractors.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge