Xuefeng Fan
DeepHider: A Multi-module and Invisibility Watermarking Scheme for Language Model
Aug 14, 2022
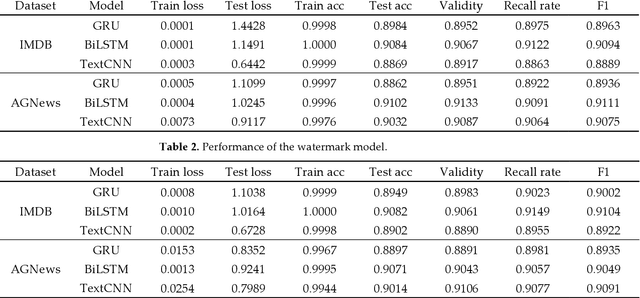
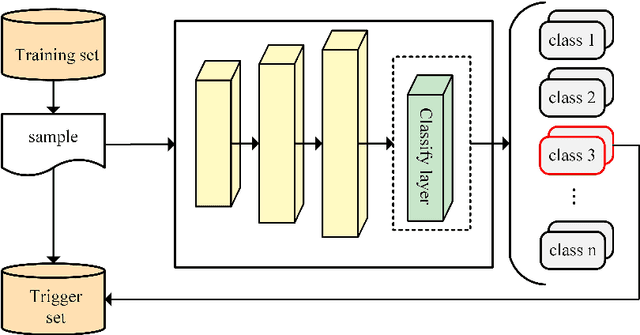
Abstract:Natural language processing (NLP) technology has shown great economic value in business. However, a natural language processing model faces two problems: (1) the owner's models of NLP are vulnerable to the threat of pirated redistribution, which breaks the symmetry relation between model owners and consumers; (2) a stealer may replace the classification module for a watermarked model to satisfy his specific classification task, and remove the watermark existing in the model. For the first problem, a model-protection mechanism is needed to keep the symmetry from being broken. Currently, language model protection schemes based on black-box verification are easily detected by humans or anomaly detectors, thus preventing verification. To address this issue, the paper proposes a trigger sample set with triggerless mode. For the second problem, this paper proposes a new threat, which is to replace the model classification module and perform global fine-tuning on the model, and verifies the model ownership through a white-box approach. Meanwhile, we use the features of blockchain such as tamper-proof and traceability to prevent the ownership statement of stealers. Experiments show that the proposed scheme successfully verifies ownership with 100% watermark verification accuracy without affecting the original performance of the model, and has strong robustness and low False trigger rate.
PCPT and ACPT: Copyright Protection and Traceability Scheme for DNN Model
Jun 06, 2022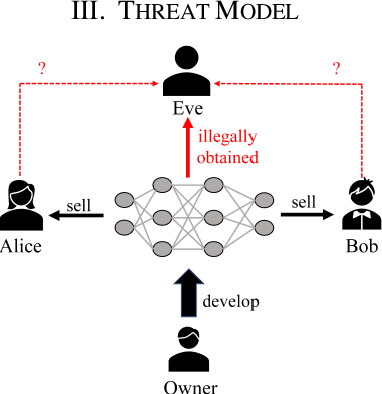
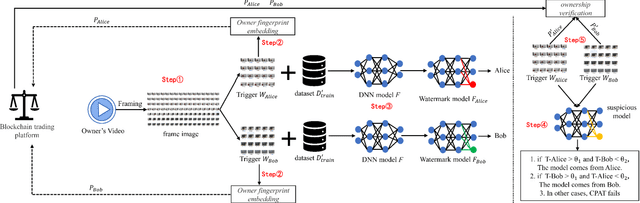
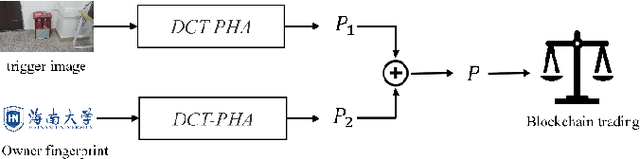
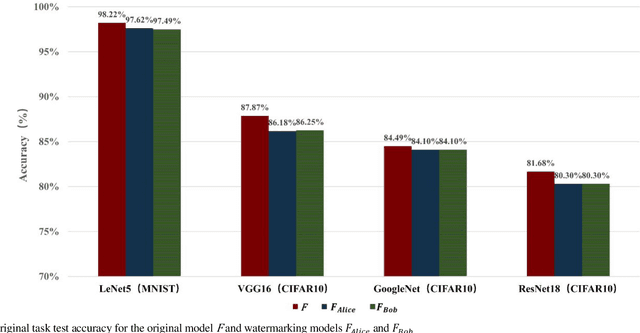
Abstract:Deep neural networks (DNNs) have achieved tremendous success in artificial intelligence (AI) fields. However, DNN models can be easily illegally copied, redistributed, or abused by criminals, seriously damaging the interests of model inventers. Currently, the copyright protection of DNN models by neural network watermarking has been studied, but the establishment of a traceability mechanism for determining the authorized users of a leaked model is a new problem driven by the demand for AI services. Because the existing traceability mechanisms are used for models without watermarks, a small number of false positives is generated. Existing black-box active protection schemes have loose authorization control and are vulnerable to forgery attacks. Therefore, based on the idea of black-box neural network watermarking with the video framing and image perceptual hash algorithm, this study proposes a passive copyright protection and traceability framework PCPT using an additional class of DNN models, improving the existing traceability mechanism that yields a small number of false positives. Based on the authorization control strategy and image perceptual hash algorithm, using the authorization control center constructed using the detector and verifier, a DNN model active copyright protection and traceability framework ACPT is proposed. It realizes stricter authorization control, which establishes a strong connection between users and model owners, and improves the framework security. The key sample that is simultaneously generated does not affect the quality of the original image and supports traceability verification.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge