Wenxin Xie
Hypernetwork Dismantling via Deep Reinforcement Learning
Apr 29, 2021
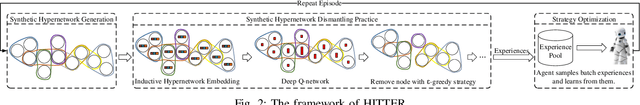
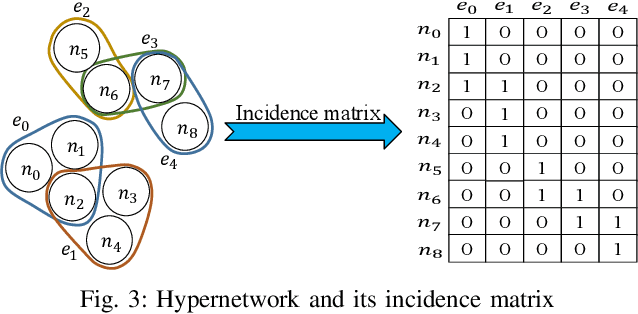
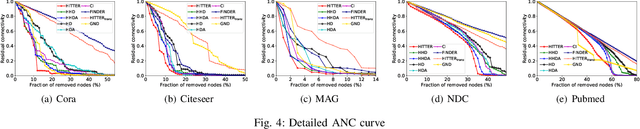
Abstract:Network dismantling aims to degrade the connectivity of a network by removing an optimal set of nodes and has been widely adopted in many real-world applications such as epidemic control and rumor containment. However, conventional methods usually focus on simple network modeling with only pairwise interactions, while group-wise interactions modeled by hypernetwork are ubiquitous and critical. In this work, we formulate the hypernetwork dismantling problem as a node sequence decision problem and propose a deep reinforcement learning (DRL)-based hypernetwork dismantling framework. Besides, we design a novel inductive hypernetwork embedding method to ensure the transferability to various real-world hypernetworks. Generally, our framework builds an agent. It first generates small-scale synthetic hypernetworks and embeds the nodes and hypernetworks into a low dimensional vector space to represent the action and state space in DRL, respectively. Then trial-and-error dismantling tasks are conducted by the agent on these synthetic hypernetworks, and the dismantling strategy is continuously optimized. Finally, the well-optimized strategy is applied to real-world hypernetwork dismantling tasks. Experimental results on five real-world hypernetworks demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed framework.
Heterogeneous Information Network-based Interest Composition with Graph Neural Network for Recommendation
Mar 11, 2021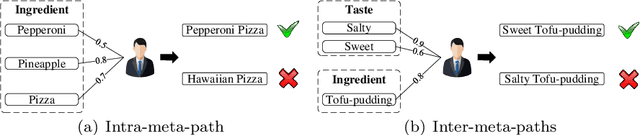
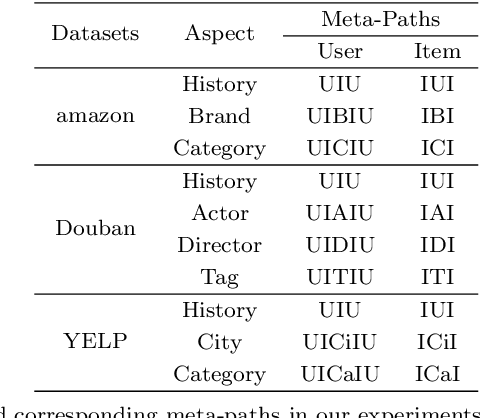
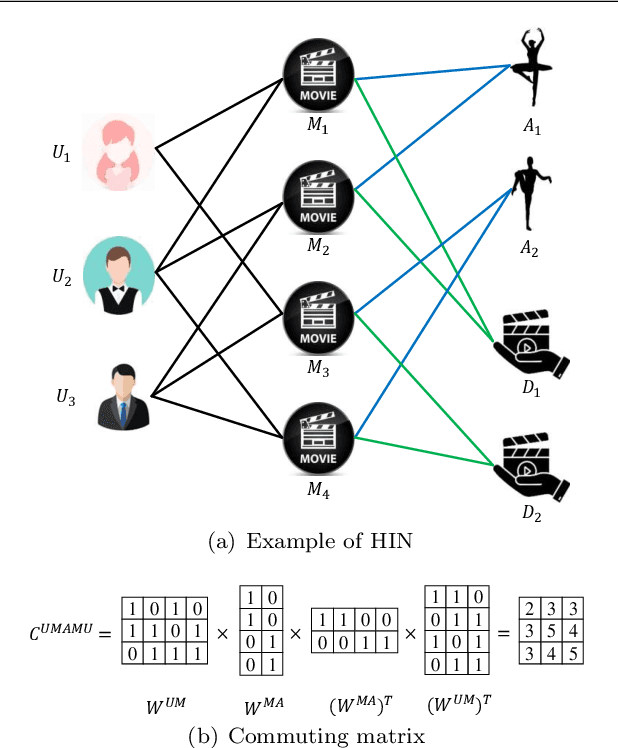
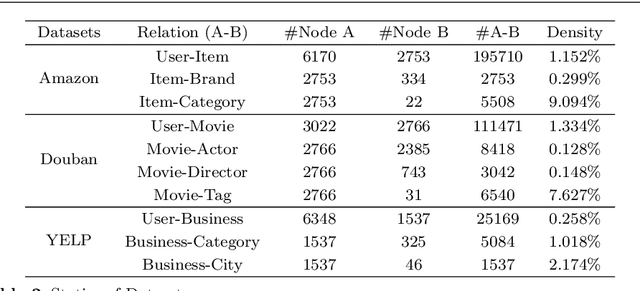
Abstract:Recommendation systems (RSs) are skilled at capturing users' preferences according to their history interactions with items, while the RSs usually suffer from the sparsity of user-item interactions. Thus, various auxiliary information is introduced to alleviate this problem. Due to powerful ability in modeling auxiliary information, the heterogeneous information network (HIN) is widely applied to the RSs. However, in existing methods, the process of information extraction from various meta-paths takes no consideration of graph structure and user/item features simultaneously. Moreover, existing models usually fuse the information from various meta-paths through simply weighted summation, while ingore the interest compositions intra- and inter-meta-paths which is capable of applying abundant high-order composition interests to RSs. Therefore, we propose a HIN-based Interest Compositions model with graph neural network for Recommendation (short for HicRec). Above all, our model learns users and items representations from various graphs corresponding to the meta-paths with the help of the graph convolution network (GCN). Then, the representations of users and items are transformed into users' interests on items. Lastly, the interests intra- and inter-meta-paths are composed and applied to recommendation. Extensive experiments are conducted on three real-world datasets and the results show that the HicRec outperforms various baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge