Wenlong Gou
Random Time-hopping Secure Ranging Strategy Against Distance-Reduction Attacks in UWB
Jun 10, 2024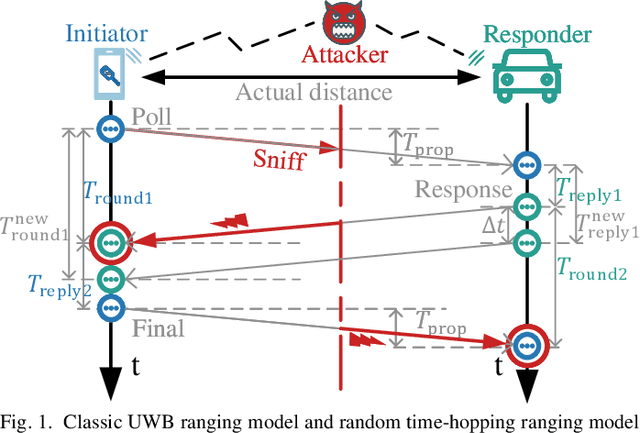
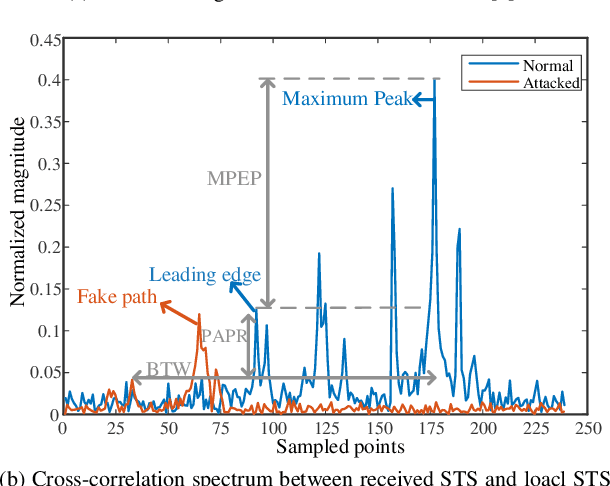
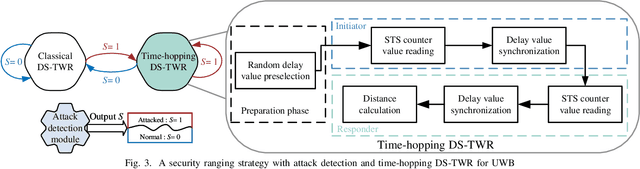
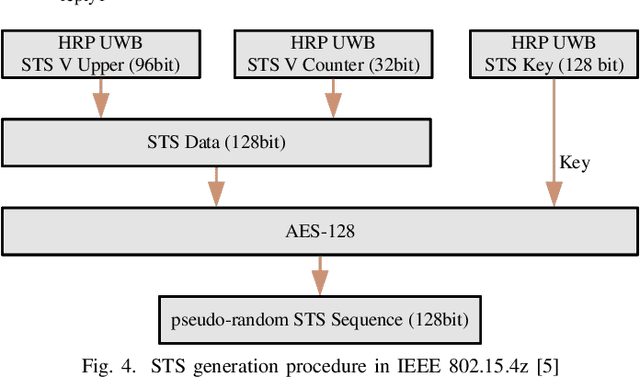
Abstract:In order to mitigate the distance reduction attack in Ultra-Wide Band (UWB) ranging, this paper proposes a secure ranging scheme based on a random time-hopping mechanism without redundant signaling overhead. Additionally, a secure ranging strategy is designed for backward compatibility with existing standards such as IEEE 802.15.4a/z, combined with an attack detection scheme. The effectiveness and feasibility of the proposed strategy are demonstrated through both simulation and experimental results in the case of the Ghost Peak attack, as demonstrated by Patrick Leu et al. The random time-hopping mechanism is verified to be capable of reducing the success rate of distance reduction attacks to less than 0.01%, thereby significantly enhancing the security of UWB ranging.
Channel Reciprocity Based Attack Detection for Securing UWB Ranging by Autoencoder
May 28, 2024Abstract:A variety of ranging threats represented by Ghost Peak attack have raised concerns regarding the security performance of Ultra-Wide Band (UWB) systems with the finalization of the IEEE 802.15.4z standard. Based on channel reciprocity, this paper proposes a low complexity attack detection scheme that compares Channel Impulse Response (CIR) features of both ranging sides utilizing an autoencoder with the capability of data compression and feature extraction. Taking Ghost Peak attack as an example, this paper demonstrates the effectiveness, feasibility and generalizability of the proposed attack detection scheme through simulation and experimental validation. The proposed scheme achieves an attack detection success rate of over 99% and can be implemented in current systems at low cost.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge