Warren Jouanneau
An Efficient Long-Context Ranking Architecture With Calibrated LLM Distillation: Application to Person-Job Fit
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Finding the most relevant person for a job proposal in real time is challenging, especially when resumes are long, structured, and multilingual. In this paper, we propose a re-ranking model based on a new generation of late cross-attention architecture, that decomposes both resumes and project briefs to efficiently handle long-context inputs with minimal computational overhead. To mitigate historical data biases, we use a generative large language model (LLM) as a teacher, generating fine-grained, semantically grounded supervision. This signal is distilled into our student model via an enriched distillation loss function. The resulting model produces skill-fit scores that enable consistent and interpretable person-job matching. Experiments on relevance, ranking, and calibration metrics demonstrate that our approach outperforms state-of-the-art baselines.
Evaluating LLM Behavior in Hiring: Implicit Weights, Fairness Across Groups, and Alignment with Human Preferences
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:General-purpose Large Language Models (LLMs) show significant potential in recruitment applications, where decisions require reasoning over unstructured text, balancing multiple criteria, and inferring fit and competence from indirect productivity signals. Yet, it is still uncertain how LLMs assign importance to each attribute and whether such assignments are in line with economic principles, recruiter preferences or broader societal norms. We propose a framework to evaluate an LLM's decision logic in recruitment, by drawing on established economic methodologies for analyzing human hiring behavior. We build synthetic datasets from real freelancer profiles and project descriptions from a major European online freelance marketplace and apply a full factorial design to estimate how a LLM weighs different match-relevant criteria when evaluating freelancer-project fit. We identify which attributes the LLM prioritizes and analyze how these weights vary across project contexts and demographic subgroups. Finally, we explain how a comparable experimental setup could be implemented with human recruiters to assess alignment between model and human decisions. Our findings reveal that the LLM weighs core productivity signals, such as skills and experience, but interprets certain features beyond their explicit matching value. While showing minimal average discrimination against minority groups, intersectional effects reveal that productivity signals carry different weights between demographic groups.
Skill matching at scale: freelancer-project alignment for efficient multilingual candidate retrieval
Sep 19, 2024Abstract:Finding the perfect match between a job proposal and a set of freelancers is not an easy task to perform at scale, especially in multiple languages. In this paper, we propose a novel neural retriever architecture that tackles this problem in a multilingual setting. Our method encodes project descriptions and freelancer profiles by leveraging pre-trained multilingual language models. The latter are used as backbone for a custom transformer architecture that aims to keep the structure of the profiles and project. This model is trained with a contrastive loss on historical data. Thanks to several experiments, we show that this approach effectively captures skill matching similarity and facilitates efficient matching, outperforming traditional methods.
A patch-based architecture for multi-label classification from single label annotations
Sep 14, 2022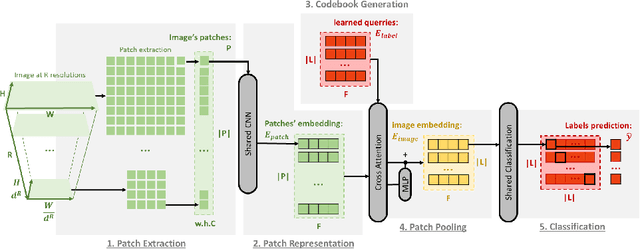
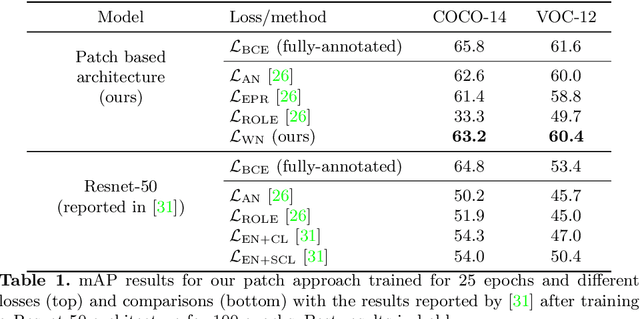
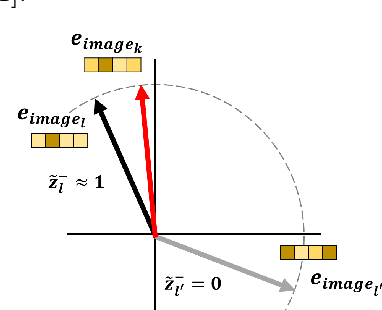

Abstract:In this paper, we propose a patch-based architecture for multi-label classification problems where only a single positive label is observed in images of the dataset. Our contributions are twofold. First, we introduce a light patch architecture based on the attention mechanism. Next, leveraging on patch embedding self-similarities, we provide a novel strategy for estimating negative examples and deal with positive and unlabeled learning problems. Experiments demonstrate that our architecture can be trained from scratch, whereas pre-training on similar databases is required for related methods from the literature.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge