Wangjin Lee
Clinical Text Generation through Leveraging Medical Concept and Relations
Oct 02, 2019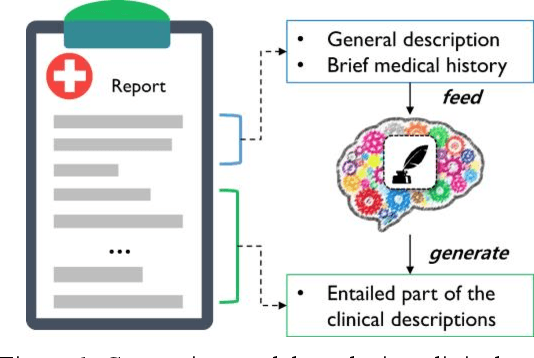
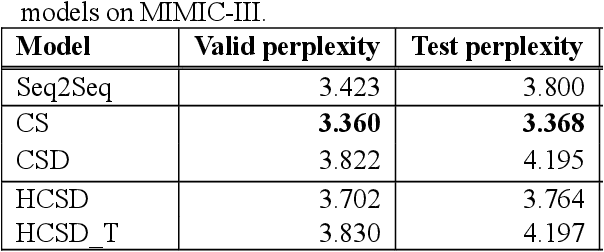
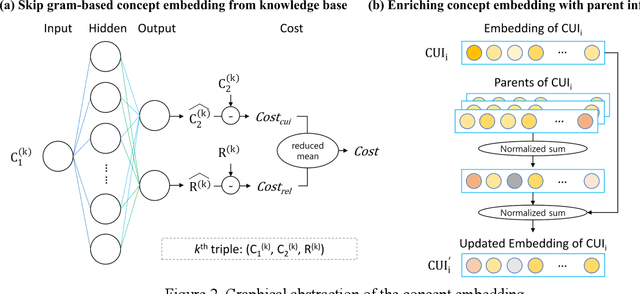
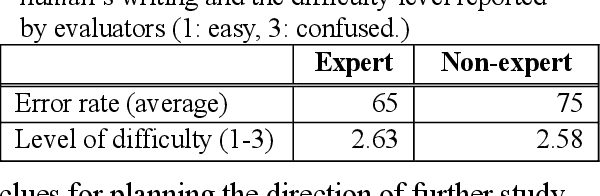
Abstract:With a neural sequence generation model, this study aims to develop a method of writing the patient clinical texts given a brief medical history. As a proof-of-a-concept, we have demonstrated that it can be workable to use medical concept embedding in clinical text generation. Our model was based on the Sequence-to-Sequence architecture and trained with a large set of de-identified clinical text data. The quantitative result shows that our concept embedding method decreased the perplexity of the baseline architecture. Also, we discuss the analyzed results from a human evaluation performed by medical doctors.
Connecting Distant Entities with Induction through Conditional Random Fields for Named Entity Recognition: Precursor-Induced CRF
May 26, 2018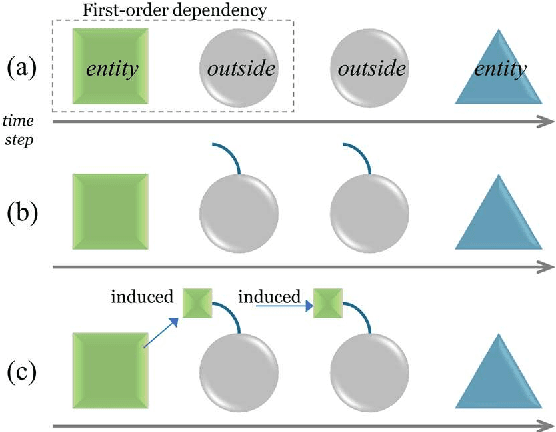
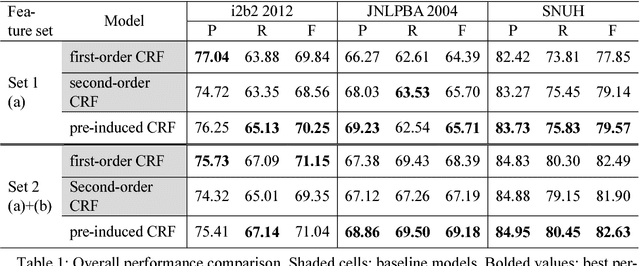
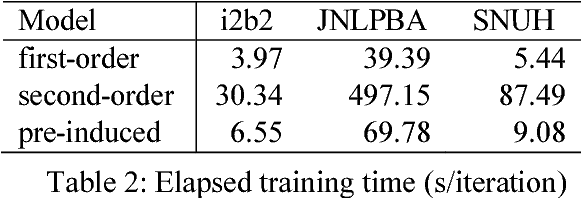
Abstract:This paper presents a method of designing specific high-order dependency factor on the linear chain conditional random fields (CRFs) for named entity recognition (NER). Named entities tend to be separated from each other by multiple outside tokens in a text, and thus the first-order CRF, as well as the second-order CRF, may innately lose transition information between distant named entities. The proposed design uses outside label in NER as a transmission medium of precedent entity information on the CRF. Then, empirical results apparently demonstrate that it is possible to exploit long-distance label dependency in the original first-order linear chain CRF structure upon NER while reducing computational loss rather than in the second-order CRF.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge