Volker Stolz
Evaluation of k-means time series clustering based on z-normalization and NP-Free
Jan 28, 2024Abstract:Despite the widespread use of k-means time series clustering in various domains, there exists a gap in the literature regarding its comprehensive evaluation with different time series normalization approaches. This paper seeks to fill this gap by conducting a thorough performance evaluation of k-means time series clustering on real-world open-source time series datasets. The evaluation focuses on two distinct normalization techniques: z-normalization and NP-Free. The former is one of the most commonly used normalization approach for time series. The latter is a real-time time series representation approach, which can serve as a time series normalization approach. The primary objective of this paper is to assess the impact of these two normalization techniques on k-means time series clustering in terms of its clustering quality. The experiments employ the silhouette score, a well-established metric for evaluating the quality of clusters in a dataset. By systematically investigating the performance of k-means time series clustering with these two normalization techniques, this paper addresses the current gap in k-means time series clustering evaluation and contributes valuable insights to the development of time series clustering.
NP-Free: A Real-Time Normalization-free and Parameter-tuning-free Representation Approach for Open-ended Time Series
Apr 12, 2023
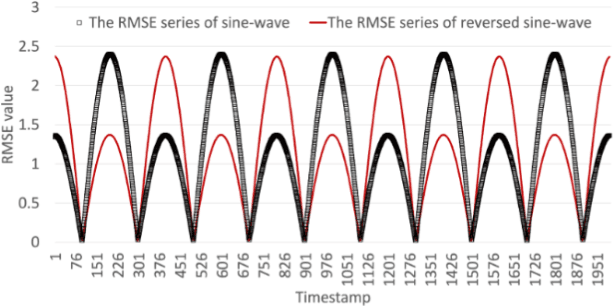
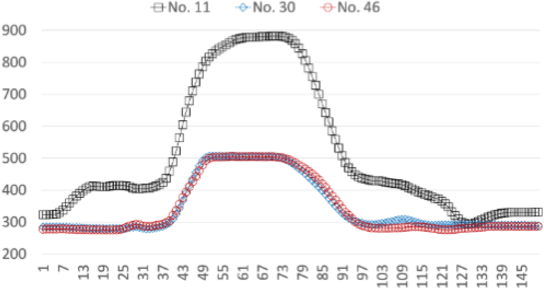
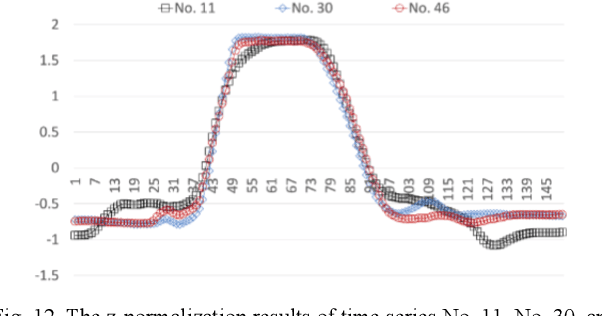
Abstract:As more connected devices are implemented in a cyber-physical world and data is expected to be collected and processed in real time, the ability to handle time series data has become increasingly significant. To help analyze time series in data mining applications, many time series representation approaches have been proposed to convert a raw time series into another series for representing the original time series. However, existing approaches are not designed for open-ended time series (which is a sequence of data points being continuously collected at a fixed interval without any length limit) because these approaches need to know the total length of the target time series in advance and pre-process the entire time series using normalization methods. Furthermore, many representation approaches require users to configure and tune some parameters beforehand in order to achieve satisfactory representation results. In this paper, we propose NP-Free, a real-time Normalization-free and Parameter-tuning-free representation approach for open-ended time series. Without needing to use any normalization method or tune any parameter, NP-Free can generate a representation for a raw time series on the fly by converting each data point of the time series into a root-mean-square error (RMSE) value based on Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) and a Look-Back and Predict-Forward strategy. To demonstrate the capability of NP-Free in representing time series, we conducted several experiments based on real-world open-source time series datasets. We also evaluated the time consumption of NP-Free in generating representations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge