Vladimir Trunov
Prediction of Locally Stationary Data Using Expert Advice
Oct 30, 2023Abstract:The problem of continuous machine learning is studied. Within the framework of the game-theoretic approach, when for calculating the next forecast, no assumptions about the stochastic nature of the source that generates the data flow are used -- the source can be analog, algorithmic or probabilistic, its parameters can change at random times, when building a prognostic model, only structural assumptions are used about the nature of data generation. An online forecasting algorithm for a locally stationary time series is presented. An estimate of the efficiency of the proposed algorithm is obtained.
Online Aggregation of Probability Forecasts with Confidence
Sep 29, 2021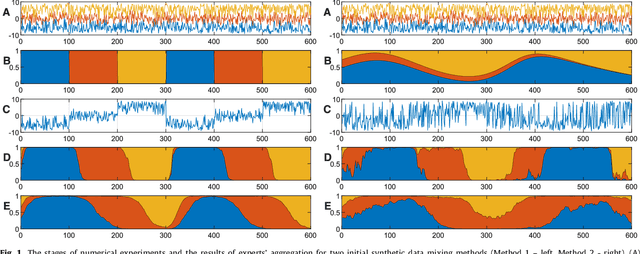
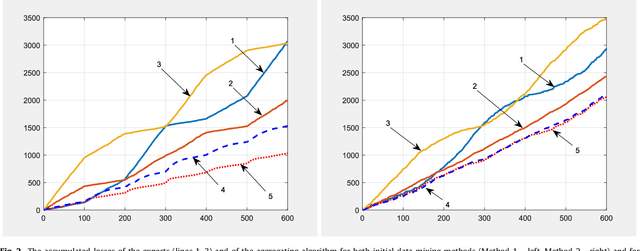
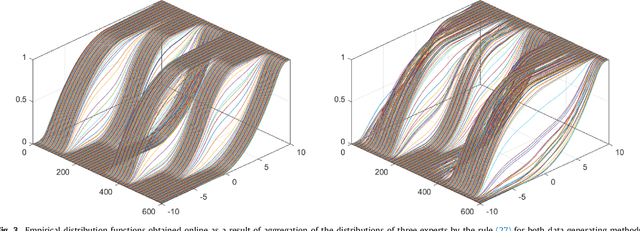
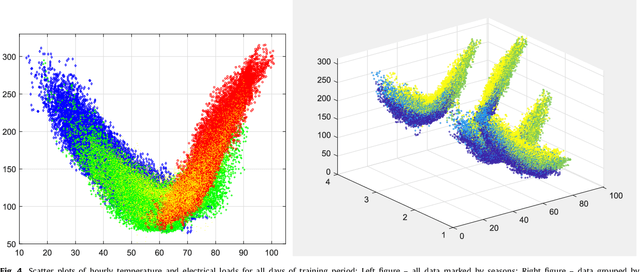
Abstract:The paper presents numerical experiments and some theoretical developments in prediction with expert advice (PEA). One experiment deals with predicting electricity consumption depending on temperature and uses real data. As the pattern of dependence can change with season and time of the day, the domain naturally admits PEA formulation with experts having different ``areas of expertise''. We consider the case where several competing methods produce online predictions in the form of probability distribution functions. The dissimilarity between a probability forecast and an outcome is measured by a loss function (scoring rule). A popular example of scoring rule for continuous outcomes is Continuous Ranked Probability Score (CRPS). In this paper the problem of combining probabilistic forecasts is considered in the PEA framework. We show that CRPS is a mixable loss function and then the time-independent upper bound for the regret of the Vovk aggregating algorithm using CRPS as a loss function can be obtained. Also, we incorporate a ``smooth'' version of the method of specialized experts in this scheme which allows us to combine the probabilistic predictions of the specialized experts with overlapping domains of their competence.
* 32 pages, 10 figures
Online Learning with Continuous Ranked Probability Score
Feb 26, 2019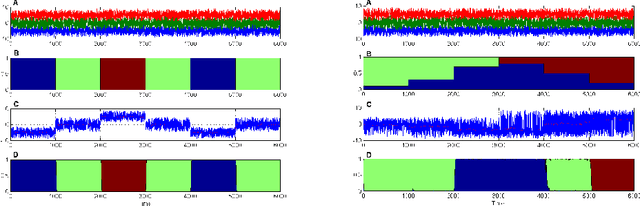
Abstract:Probabilistic forecasts in the form of probability distributions over future events have become popular in several fields of statistical science. The dissimilarity between a probability forecast and an outcome is measured by a loss function (scoring rule). Popular example of scoring rule for continuous outcomes is the continuous ranked probability score (CRPS). We consider the case where several competing methods produce online predictions in the form of probability distribution functions. In this paper, the problem of combining probabilistic forecasts is considered in the prediction with expert advice framework. We show that CRPS is a mixable loss function and then the time independent upper bound for the regret of the Vovk's aggregating algorithm using CRPS as a loss function can be obtained. We present the results of numerical experiments illustrating the proposed methods.
Online Aggregation of Unbounded Losses Using Shifting Experts with Confidence
Sep 30, 2018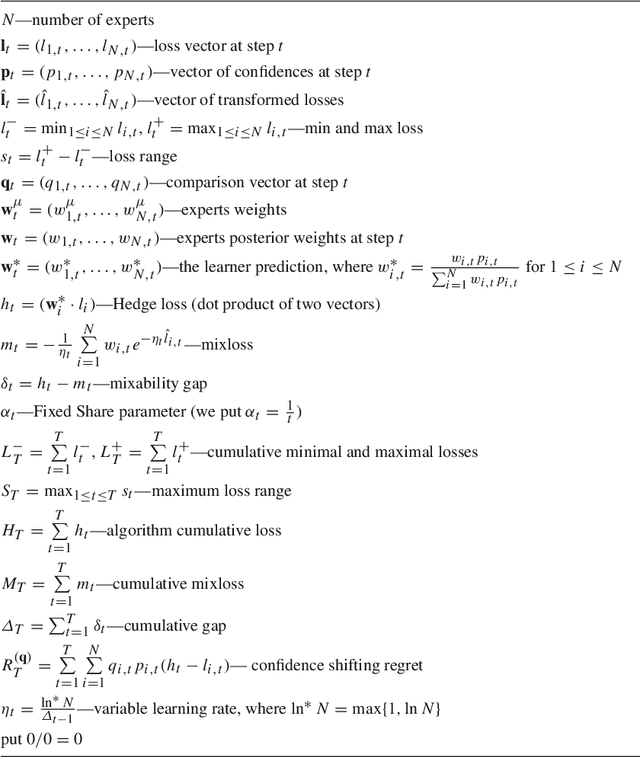
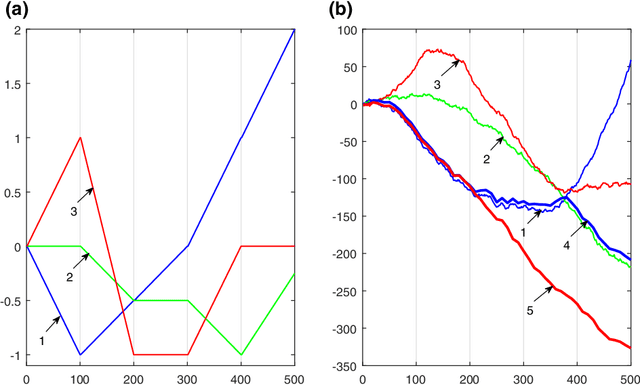
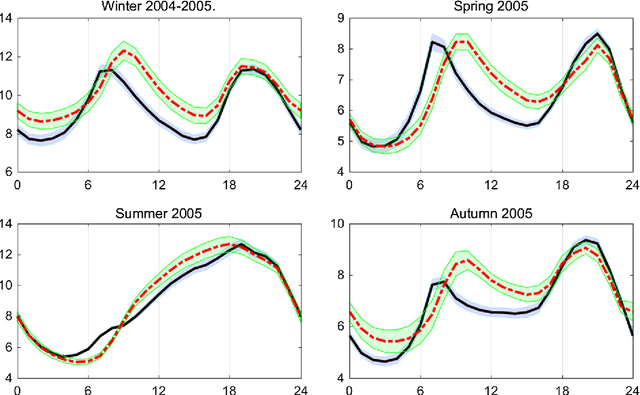
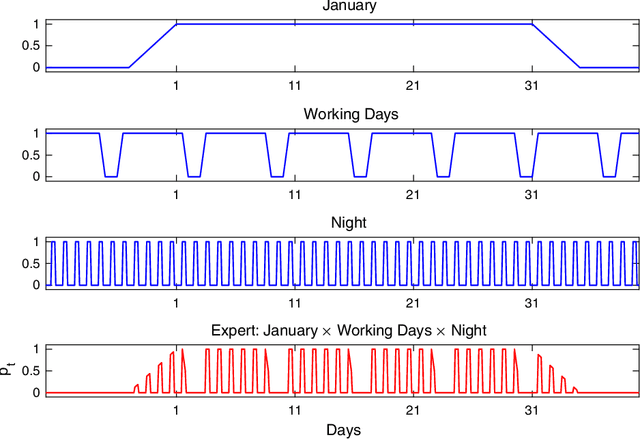
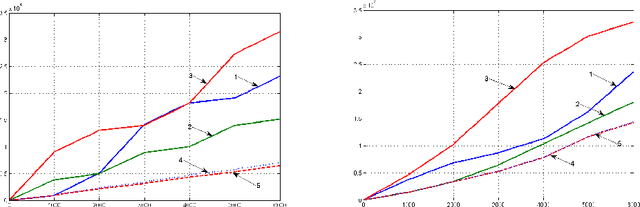
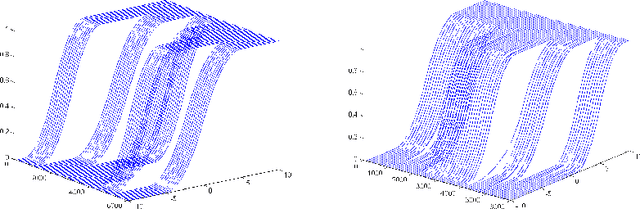
Abstract:We develop the setting of sequential prediction based on shifting experts and on a "smooth" version of the method of specialized experts. To aggregate experts predictions, we use the AdaHedge algorithm, which is a version of the Hedge algorithm with adaptive learning rate, and extend it by the meta-algorithm Fixed Share. Due to this, we combine the advantages of both algorithms: (1) we use the shifting regret which is a more optimal characteristic of the algorithm; (2) regret bounds are valid in the case of signed unbounded losses of the experts. Also, (3) we incorporate in this scheme a "smooth" version of the method of specialized experts which allows us to make more flexible and accurate predictions. All results are obtained in the adversarial setting -- no assumptions are made about the nature of data source. We present results of numerical experiments for short-term forecasting of electricity consumption based on a real data.
Universal Algorithm for Online Trading Based on the Method of Calibration
Nov 04, 2014
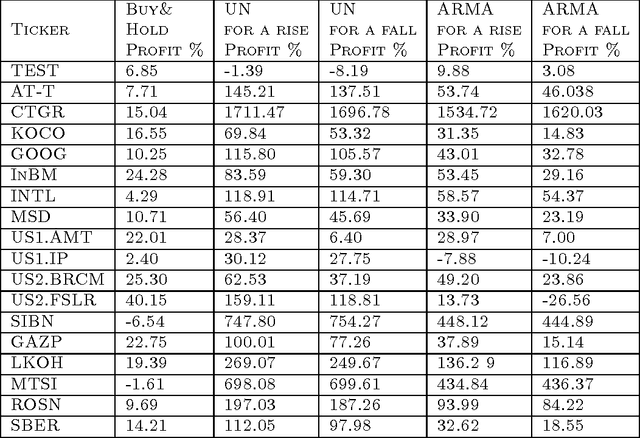
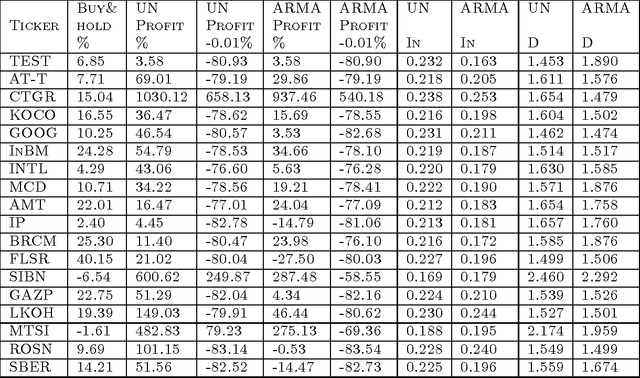
Abstract:We present a universal algorithm for online trading in Stock Market which performs asymptotically at least as good as any stationary trading strategy that computes the investment at each step using a fixed function of the side information that belongs to a given RKHS (Reproducing Kernel Hilbert Space). Using a universal kernel, we extend this result for any continuous stationary strategy. In this learning process, a trader rationally chooses his gambles using predictions made by a randomized well-calibrated algorithm. Our strategy is based on Dawid's notion of calibration with more general checking rules and on some modification of Kakade and Foster's randomized rounding algorithm for computing the well-calibrated forecasts. We combine the method of randomized calibration with Vovk's method of defensive forecasting in RKHS. Unlike the statistical theory, no stochastic assumptions are made about the stock prices. Our empirical results on historical markets provide strong evidence that this type of technical trading can "beat the market" if transaction costs are ignored.
Calibration with Changing Checking Rules and Its Application to Short-Term Trading
May 21, 2011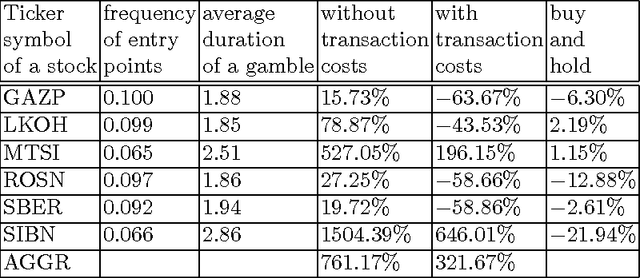
Abstract:We provide a natural learning process in which a financial trader without a risk receives a gain in case when Stock Market is inefficient. In this process, the trader rationally choose his gambles using a prediction made by a randomized calibrated algorithm. Our strategy is based on Dawid's notion of calibration with more general changing checking rules and on some modification of Kakade and Foster's randomized algorithm for computing calibrated forecasts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge