Vlad Shmerko
Intelligent Stress Assessment for e-Coaching
Nov 03, 2023Abstract:This paper considers the adaptation of the e-coaching concept at times of emergencies and disasters, through aiding the e-coaching with intelligent tools for monitoring humans' affective state. The states such as anxiety, panic, avoidance, and stress, if properly detected, can be mitigated using the e-coaching tactic and strategy. In this work, we focus on a stress monitoring assistant tool developed on machine learning techniques. We provide the results of an experimental study using the proposed method.
Fairness on Synthetic Visual and Thermal Mask Images
Sep 19, 2022
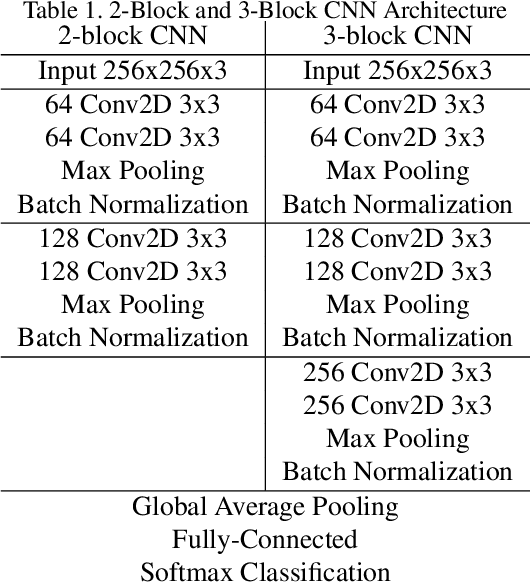
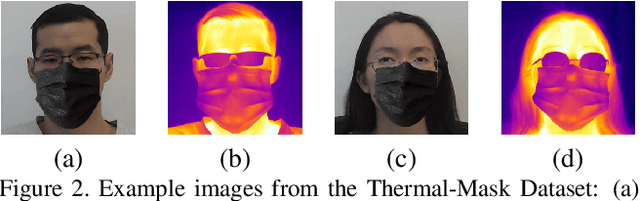
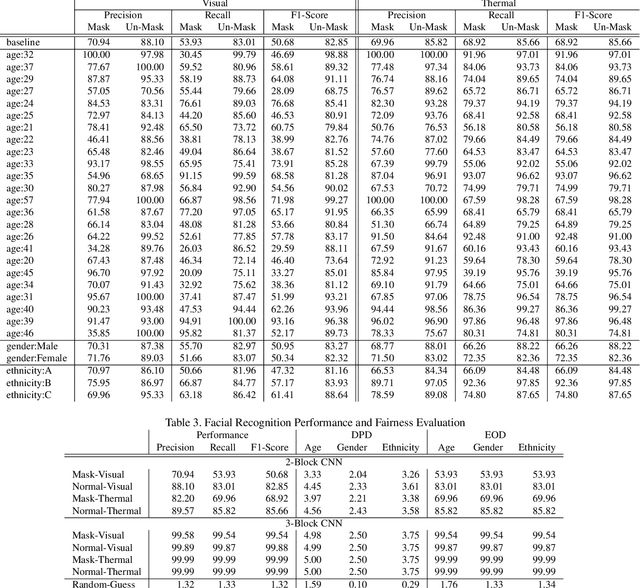
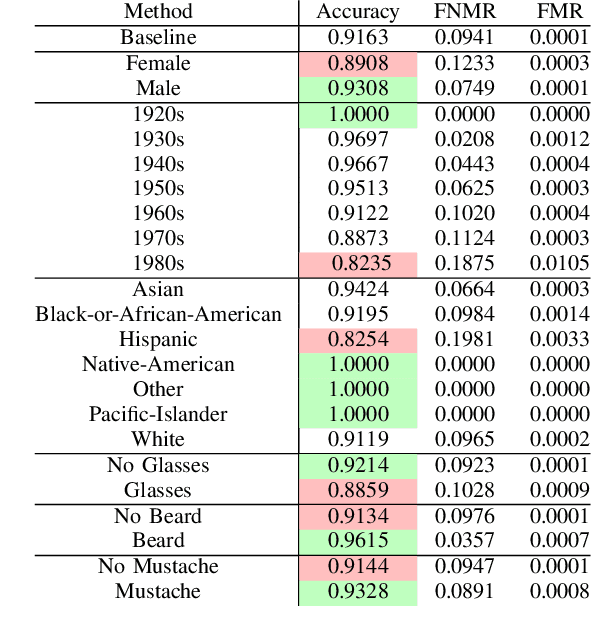
Abstract:In this paper, we study performance and fairness on visual and thermal images and expand the assessment to masked synthetic images. Using the SpeakingFace and Thermal-Mask dataset, we propose a process to assess fairness on real images and show how the same process can be applied to synthetic images. The resulting process shows a demographic parity difference of 1.59 for random guessing and increases to 5.0 when the recognition performance increases to a precision and recall rate of 99.99\%. We indicate that inherently biased datasets can deeply impact the fairness of any biometric system. A primary cause of a biased dataset is the class imbalance due to the data collection process. To address imbalanced datasets, the classes with fewer samples can be augmented with synthetic images to generate a more balanced dataset resulting in less bias when training a machine learning system. For biometric-enabled systems, fairness is of critical importance, while the related concept of Equity, Diversity, and Inclusion (EDI) is well suited for the generalization of fairness in biometrics, in this paper, we focus on the 3 most common demographic groups age, gender, and ethnicity.
Biometrics in the Time of Pandemic: 40% Masked Face Recognition Degradation can be Reduced to 2%
Jan 03, 2022



Abstract:In this study of the face recognition on masked versus unmasked faces generated using Flickr-Faces-HQ and SpeakingFaces datasets, we report 36.78% degradation of recognition performance caused by the mask-wearing at the time of pandemics, in particular, in border checkpoint scenarios. We have achieved better performance and reduced the degradation to 1.79% using advanced deep learning approaches in the cross-spectral domain.
Counter-Epidemiological Projections of e-Coaching
May 24, 2021



Abstract:This paper considers e-coaching at times of pandemic. It utilizes the Emergency Management Cycle (EMC), a core doctrine for managing disasters. The EMC dimensions provide a useful taxonomical view for the development and application of e-coaching systems, emphasizing technological and societal issues. Typical pandemic symptoms such as anxiety, panic, avoidance, and stress, if properly detected, can be mitigated using the e-coaching tactic and strategy. In this work, we focus on a stress monitoring assistant developed upon machine learning techniques. We provide the results of an experimental study of a prototype of such an assistant. Our study leads to the conclusion that stress monitoring shall become a valuable component of e-coaching at all EMC phases.
Reliability of Decision Support in Cross-spectral Biometric-enabled Systems
Aug 13, 2020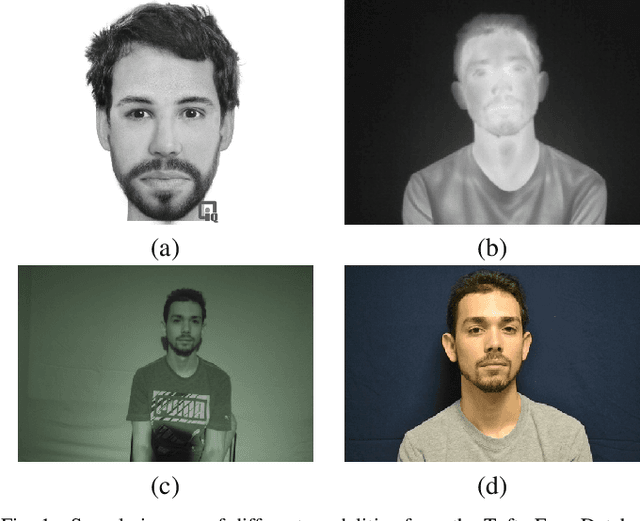
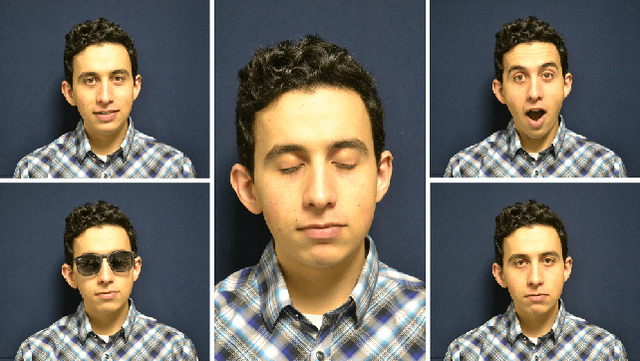
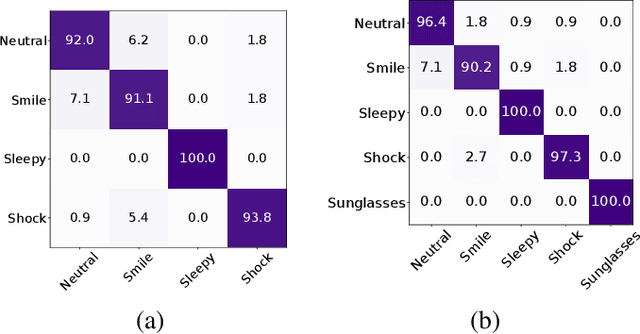
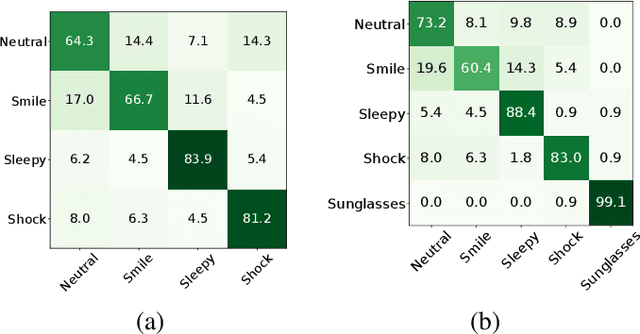
Abstract:This paper addresses the evaluation of the performance of the decision support system that utilizes face and facial expression biometrics. The evaluation criteria include risk of error and related reliability of decision, as well as their contribution to the changes in the perceived operator's trust in the decision. The relevant applications include human behavior monitoring and stress detection in individuals and teams, and in situational awareness system. Using an available database of cross-spectral videos of faces and facial expressions, we conducted a series of experiments that demonstrate the phenomenon of biases in biometrics that affect the evaluated measures of the performance in human-machine systems.
On the Gap between Epidemiological Surveillance and Preparedness
Aug 10, 2020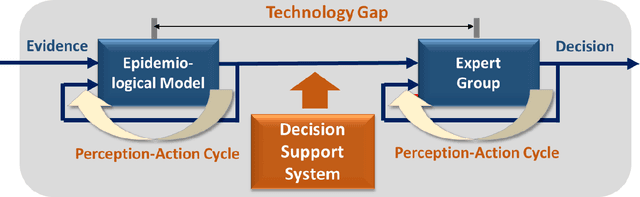
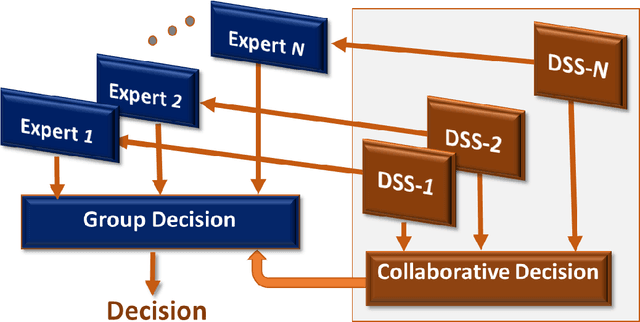
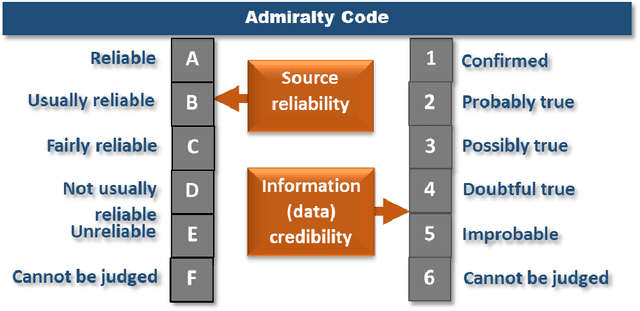
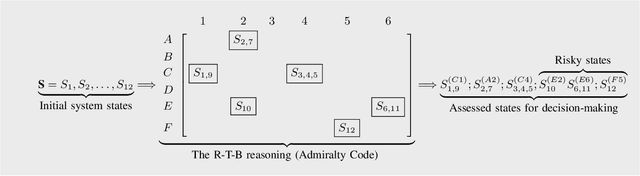
Abstract:Contemporary Epidemiological Surveillance (ES) relies heavily on data analytics. These analytics are critical input for pandemics preparedness networks; however, this input is not integrated into a form suitable for decision makers or experts in preparedness. A decision support system (DSS) with Computational Intelligence (CI) tools is required to bridge the gap between epidemiological model of evidence and expert group decision. We argue that such DSS shall be a cognitive dynamic system enabling the CI and human expert to work together. The core of such DSS must be based on machine reasoning techniques such as probabilistic inference, and shall be capable of estimating risks, reliability and biases in decision making.
Assessing Risks of Biases in Cognitive Decision Support Systems
Jul 28, 2020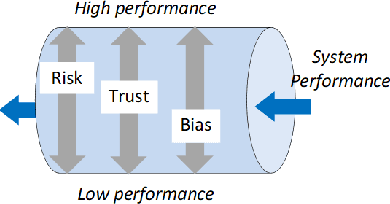

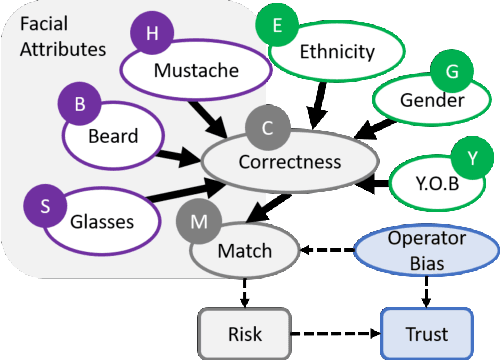
Abstract:Recognizing, assessing, countering, and mitigating the biases of different nature from heterogeneous sources is a critical problem in designing a cognitive Decision Support System (DSS). An example of such a system is a cognitive biometric-enabled security checkpoint. Biased algorithms affect the decision-making process in an unpredictable way, e.g. face recognition for different demographic groups may severely impact the risk assessment at a checkpoint. This paper addresses a challenging research question on how to manage an ensemble of biases? We provide performance projections of the DSS operational landscape in terms of biases. A probabilistic reasoning technique is used for assessment of the risk of such biases. We also provide a motivational experiment using face biometric component of the checkpoint system which highlights the discovery of an ensemble of biases and the techniques to assess their risks.
Risk Assessment in the Face-based Watchlist Screening in e-Border
Jul 22, 2020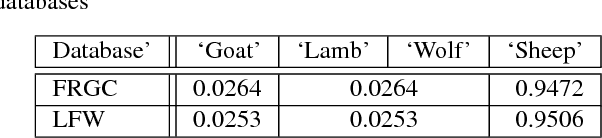
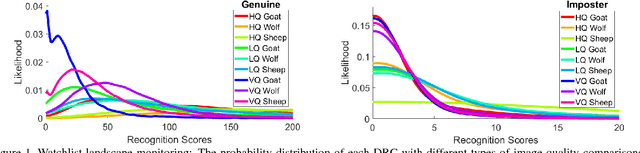
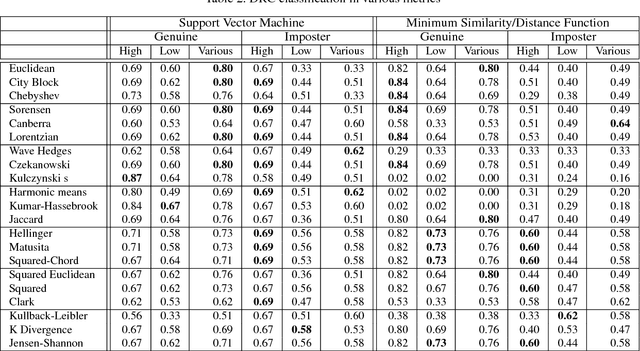

Abstract:This paper concerns with facial-based watchlist technology as a component of automated border control machines deployed in e-borders. The key task of the watchlist technology is to mitigate effects of mis-identification and impersonation. To address this problem, we developed a novel cost-based model of traveler risk assessment and proved its efficiency via intensive experiments using large-scale facial databases. The results of this study are applicable to any biometric modality to be used in watchlist technology.
Emerging Biometrics: Deep Inference and Other Computational Intelligence
Jun 22, 2020
Abstract:This paper aims at identifying emerging computational intelligence trends for the design and modeling of complex biometric-enabled infrastructure and systems. Biometric-enabled systems are evolving towards deep learning and deep inference using the principles of adaptive computing, - the front tides of the modern computational intelligence domain. Therefore, we focus on intelligent inference engines widely deployed in biometrics. Computational intelligence applications that cover a wide spectrum of biometric tasks using physiological and behavioral traits are chosen for illustration. We highlight the technology gaps that must be addressed in future generations of biometric systems. The reported approaches and results primarily address the researchers who work towards developing the next generation of intelligent biometric-enabled systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge