Vlad Atanasiu
Legibility Enhancement of Papyri Using Color Processing and Visual Illusions: A Case Study in Critical Vision
Mar 11, 2021
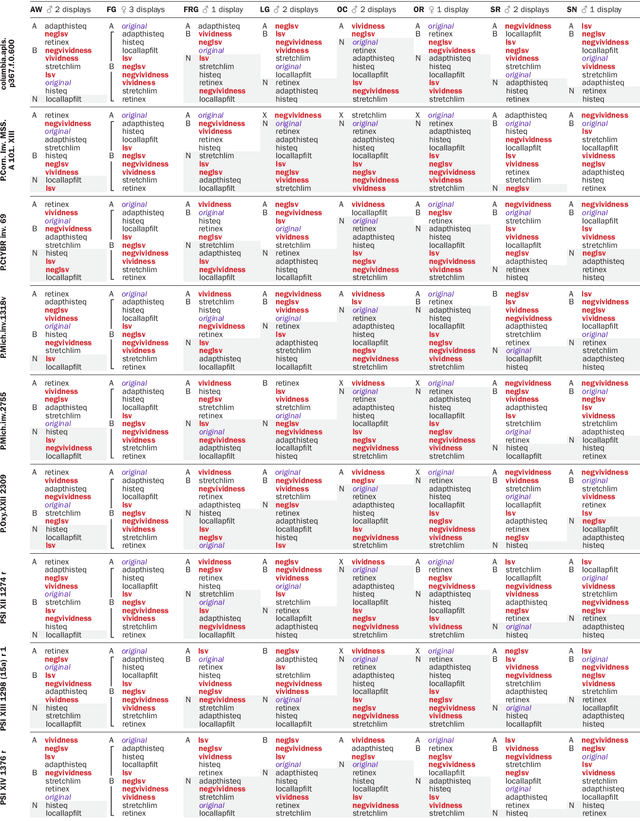

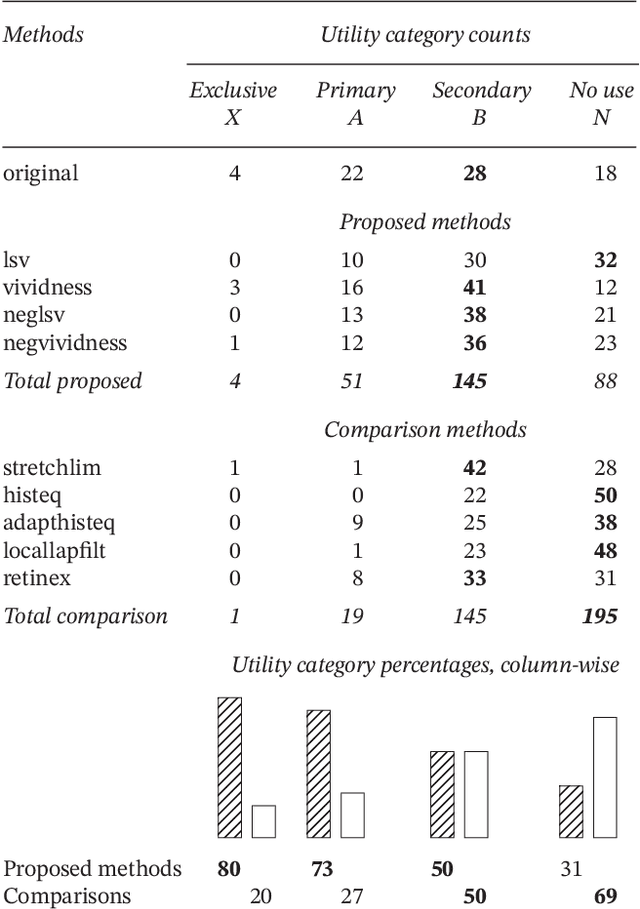
Abstract:Purpose: This article develops theoretical, algorithmic, perceptual, and interaction aspects of script legibility enhancement in the visible light spectrum for the purpose of scholarly editing of papyri texts. - Methods: Novel legibility enhancement algorithms based on color processing and visual illusions are proposed and compared to classic methods. A user experience experiment was carried out to evaluate the solutions and better understand the problem on an empirical basis. - Results: (1) The proposed methods outperformed the comparison methods. (2) The methods that most successfully enhanced script legibility were those that leverage human perception. (3) Users exhibited a broad behavioral spectrum of text-deciphering strategies, under the influence of factors such as personality and social conditioning, tasks and application domains, expertise level and image quality, and affordances of software, hardware, and interfaces. No single method satisfied all factor configurations. Therefore, using synergetically a range of enhancement methods and interaction modalities is suggested for optimal results and user satisfaction. (4) A paradigm of legibility enhancement for critical applications is outlined, comprising the following criteria: interpreting images skeptically; approaching enhancement as a system problem; considering all image structures as potential information; deriving interpretations from connections across distinct spatial locations; and making uncertainty and alternative interpretations explicit, both visually and numerically.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge