Vasileios Gkolemis
Extending the statistical software package Engine for Likelihood-Free Inference
Nov 08, 2020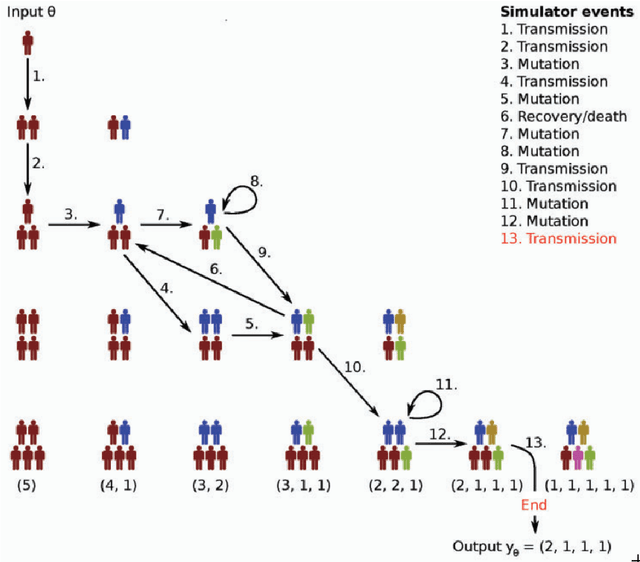

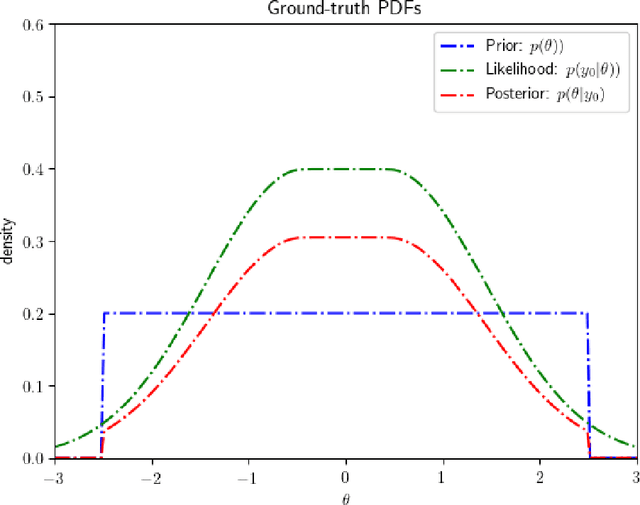
Abstract:Bayesian inference is a principled framework for dealing with uncertainty. The practitioner can perform an initial assumption for the physical phenomenon they want to model (prior belief), collect some data and then adjust the initial assumption in the light of the new evidence (posterior belief). Approximate Bayesian Computation (ABC) methods, also known as likelihood-free inference techniques, are a class of models used for performing inference when the likelihood is intractable. The unique requirement of these models is a black-box sampling machine. Due to the modelling-freedom they provide these approaches are particularly captivating. Robust Optimisation Monte Carlo (ROMC) is one of the most recent techniques of the specific domain. It approximates the posterior distribution by solving independent optimisation problems. This dissertation focuses on the implementation of the ROMC method in the software package Engine for Likelihood-Free Inference (ELFI). In the first chapters, we provide the mathematical formulation and the algorithmic description of the ROMC approach. In the following chapters, we describe our implementation; (a) we present all the functionalities provided to the user and (b) we demonstrate how to perform inference on some real examples. Our implementation provides a robust and efficient solution to a practitioner who wants to perform inference on a simulator-based model. Furthermore, it exploits parallel processing for accelerating the inference wherever it is possible. Finally, it has been designed to serve extensibility; the user can easily replace specific subparts of the method without significant overhead on the development side. Therefore, it can be used by a researcher for further experimentation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge