Vanita Jain
Pipeline for 3D reconstruction of the human body from AR/VR headset mounted egocentric cameras
Nov 09, 2021



Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel pipeline for the 3D reconstruction of the full body from egocentric viewpoints. 3-D reconstruction of the human body from egocentric viewpoints is a challenging task as the view is skewed and the body parts farther from the cameras are occluded. One such example is the view from cameras installed below VR headsets. To achieve this task, we first make use of conditional GANs to translate the egocentric views to full body third-person views. This increases the comprehensibility of the image and caters to occlusions. The generated third-person view is further sent through the 3D reconstruction module that generates a 3D mesh of the body. We also train a network that can take the third person full-body view of the subject and generate the texture maps for applying on the mesh. The generated mesh has fairly realistic body proportions and is fully rigged allowing for further applications such as real-time animation and pose transfer in games. This approach can be key to a new domain of mobile human telepresence.
Sketch2Code: Transformation of Sketches to UI in Real-time Using Deep Neural Network
Oct 20, 2019
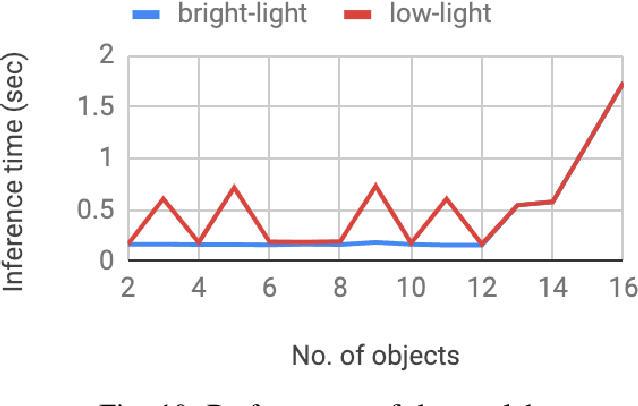
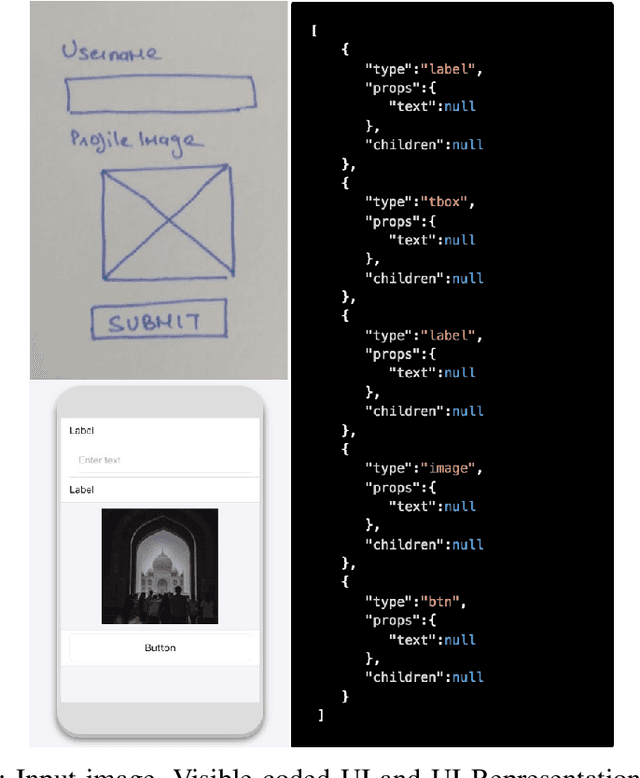
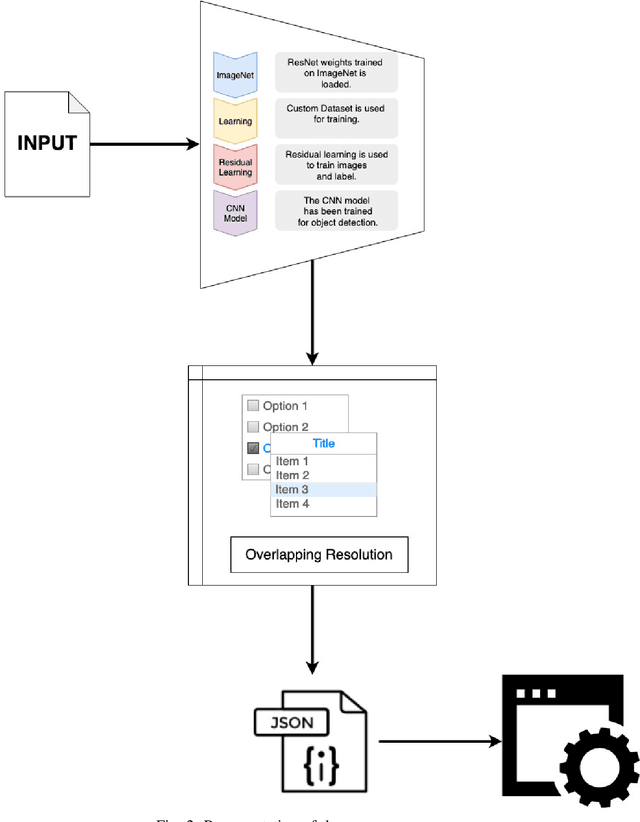
Abstract:User Interface (UI) prototyping is a necessary step in the early stages of application development. Transforming sketches of a Graphical User Interface (UI) into a coded UI application is an uninspired but time-consuming task performed by a UI designer. An automated system that can replace human efforts for straightforward implementation of UI designs will greatly speed up this procedure. The works that propose such a system primarily focus on using UI wireframes as input rather than hand-drawn sketches. In this paper, we put forward a novel approach wherein we employ a Deep Neural Network that is trained on our custom database of such sketches to detect UI elements in the input sketch. Detection of objects in sketches is a peculiar visual recognition task that requires a specific solution that our deep neural network model attempts to provide. The output from the network is a platform-independent UI representation object. The UI representation object is a dictionary of key-value pairs to represent the UI elements recognized along with their properties. This is further consumed by our UI parser which creates code for different platforms. The intrinsic platform-independence allows the model to create a UI prototype for multiple platforms with single training. This two-step approach without the need for two trained models improves over other methods giving time-efficient results (average time: 129 ms) with good accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge