Ulla Bergsten
Beslutstödssystemet Dezzy - en översikt
May 16, 2003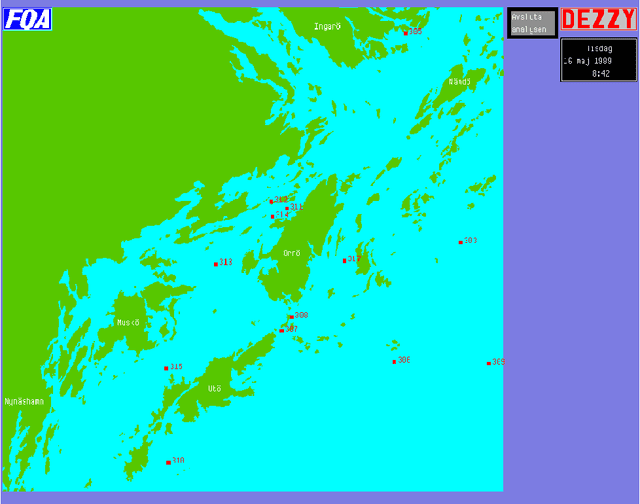
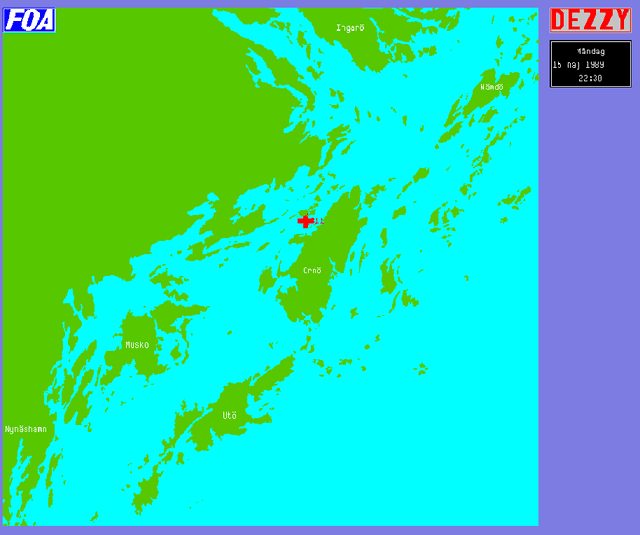
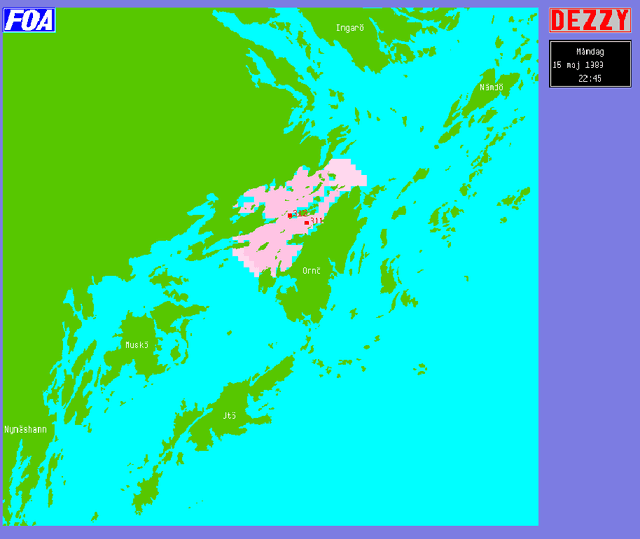
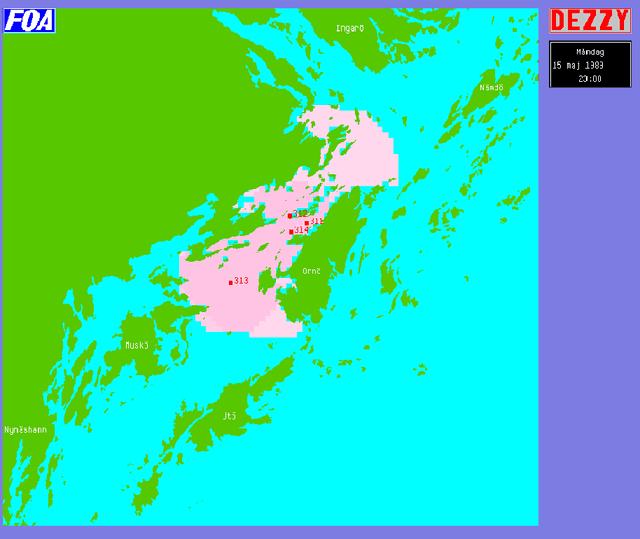
Abstract:Within the scope of the three-year ANTI-SUBMARINE WARFARE project of the National Defence Research Establishment, the INFORMATION SYSTEMS subproject has developed the demonstration prototype Dezzy for handling and analysis of intelligence reports concerning foreign underwater activities. ----- Inom ramen f\"or FOA:s tre{\aa}riga huvudprojekt UB{\AA}TSSKYDD har delprojekt INFORMATIONSSYSTEM utvecklat demonstrationsprototypen Dezzy till ett beslutsst\"odsystem f\"or hantering och analys av underr\"attelser om fr\"ammande undervattensverksamhet.
* 18 pages, 8 figures, in Swedish, with appendix in English
Applying Data Mining and Machine Learning Techniques to Submarine Intelligence Analysis
May 16, 2003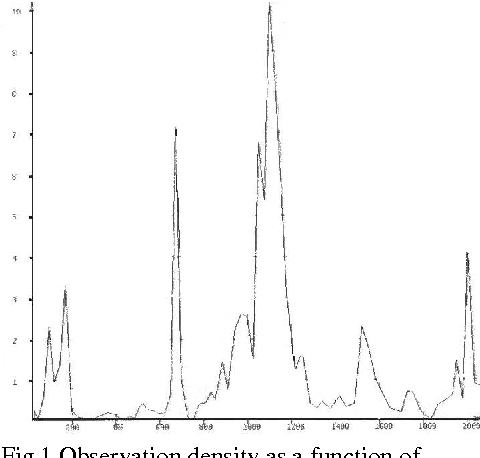
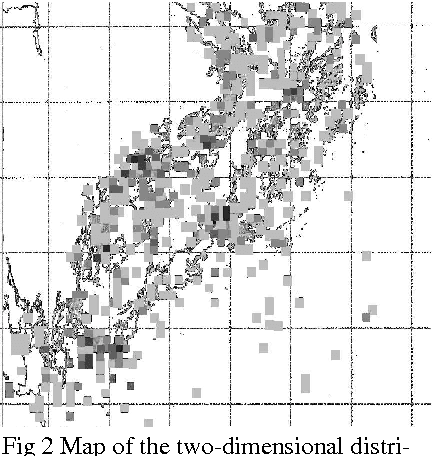
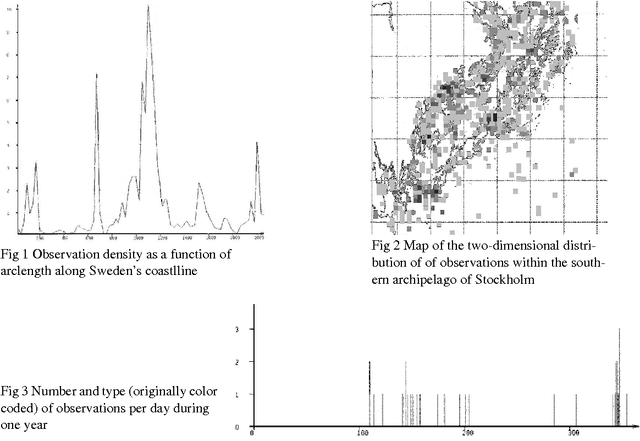
Abstract:We describe how specialized database technology and data analysis methods were applied by the Swedish defense to help deal with the violation of Swedish marine territory by foreign submarine intruders during the Eighties and early Nineties. Among several approaches tried some yielded interesting information, although most of the key questions remain unanswered. We conclude with a survey of belief-function- and genetic-algorithm-based methods which were proposed to support interpretation of intelligence reports and prediction of future submarine positions, respectively.
* 4 pages, 7 figures
Dempster's Rule for Evidence Ordered in a Complete Directed Acyclic Graph
May 16, 2003



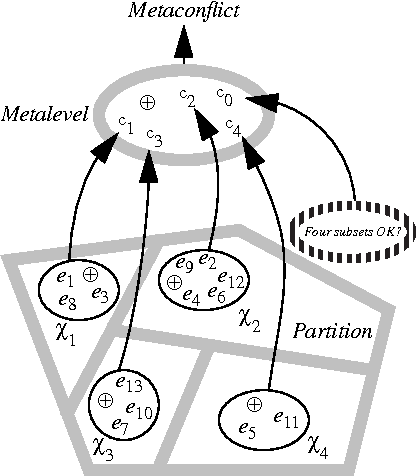
Abstract:For the case of evidence ordered in a complete directed acyclic graph this paper presents a new algorithm with lower computational complexity for Dempster's rule than that of step-by-step application of Dempster's rule. In this problem, every original pair of evidences, has a corresponding evidence against the simultaneous belief in both propositions. In this case, it is uncertain whether the propositions of any two evidences are in logical conflict. The original evidences are associated with the vertices and the additional evidences are associated with the edges. The original evidences are ordered, i.e., for every pair of evidences it is determinable which of the two evidences is the earlier one. We are interested in finding the most probable completely specified path through the graph, where transitions are possible only from lower- to higher-ranked vertices. The path is here a representation for a sequence of states, for instance a sequence of snapshots of a physical object's track. A completely specified path means that the path includes no other vertices than those stated in the path representation, as opposed to an incompletely specified path that may also include other vertices than those stated. In a hierarchical network of all subsets of the frame, i.e., of all incompletely specified paths, the original and additional evidences support subsets that are not disjoint, thus it is not possible to prune the network to a tree. Instead of propagating belief, the new algorithm reasons about the logical conditions of a completely specified path through the graph. The new algorithm is O(|THETA| log |THETA|), compared to O(|THETA| ** log |THETA|) of the classic brute force algorithm.
* 37 pages, 12 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge