Triet Minh Thai
Integrating Image Features with Convolutional Sequence-to-sequence Network for Multilingual Visual Question Answering
Mar 22, 2023


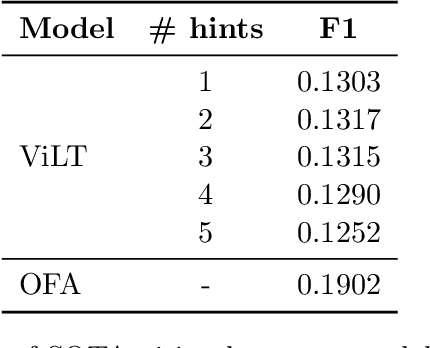
Abstract:Visual Question Answering (VQA) is a task that requires computers to give correct answers for the input questions based on the images. This task can be solved by humans with ease but is a challenge for computers. The VLSP2022-EVJVQA shared task carries the Visual Question Answering task in the multilingual domain on a newly released dataset: UIT-EVJVQA, in which the questions and answers are written in three different languages: English, Vietnamese and Japanese. We approached the challenge as a sequence-to-sequence learning task, in which we integrated hints from pre-trained state-of-the-art VQA models and image features with Convolutional Sequence-to-Sequence network to generate the desired answers. Our results obtained up to 0.3442 by F1 score on the public test set, 0.4210 on the private test set, and placed 3rd in the competition.
UIT-ViCoV19QA: A Dataset for COVID-19 Community-based Question Answering on Vietnamese Language
Sep 14, 2022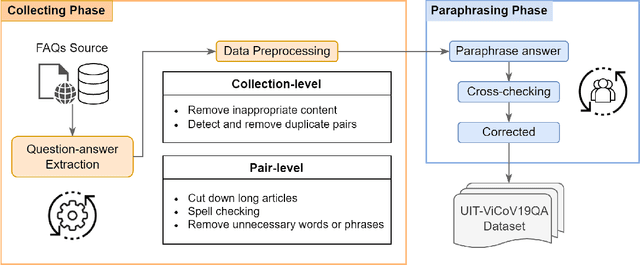
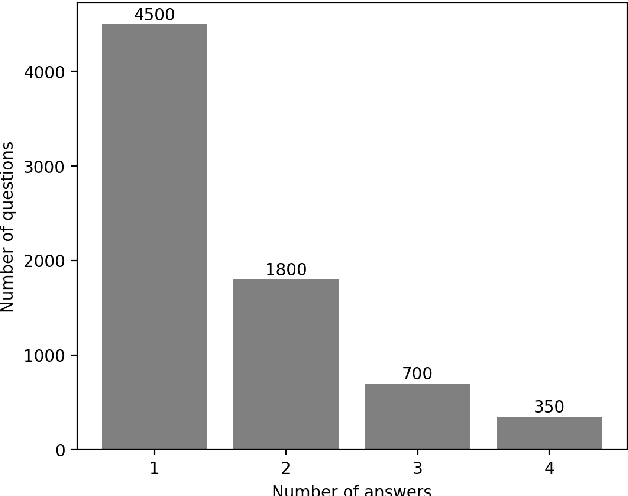
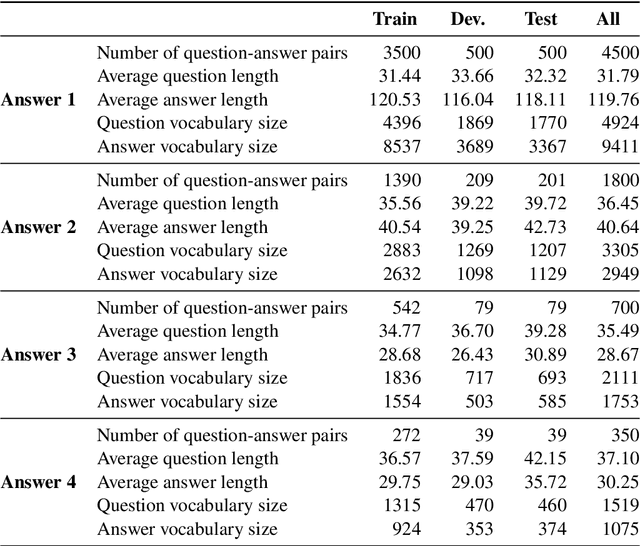

Abstract:For the last two years, from 2020 to 2021, COVID-19 has broken disease prevention measures in many countries, including Vietnam, and negatively impacted various aspects of human life and the social community. Besides, the misleading information in the community and fake news about the pandemic are also serious situations. Therefore, we present the first Vietnamese community-based question answering dataset for developing question answering systems for COVID-19 called UIT-ViCoV19QA. The dataset comprises 4,500 question-answer pairs collected from trusted medical sources, with at least one answer and at most four unique paraphrased answers per question. Along with the dataset, we set up various deep learning models as baseline to assess the quality of our dataset and initiate the benchmark results for further research through commonly used metrics such as BLEU, METEOR, and ROUGE-L. We also illustrate the positive effects of having multiple paraphrased answers experimented on these models, especially on Transformer - a dominant architecture in the field of study.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge