Tongxin Zhou
Lucy
Spoiled for Choice? Personalized Recommendation for Healthcare Decisions: A Multi-Armed Bandit Approach
Sep 13, 2020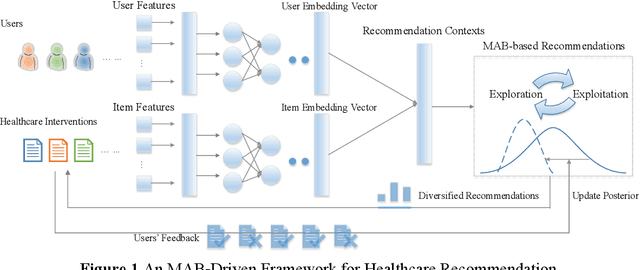
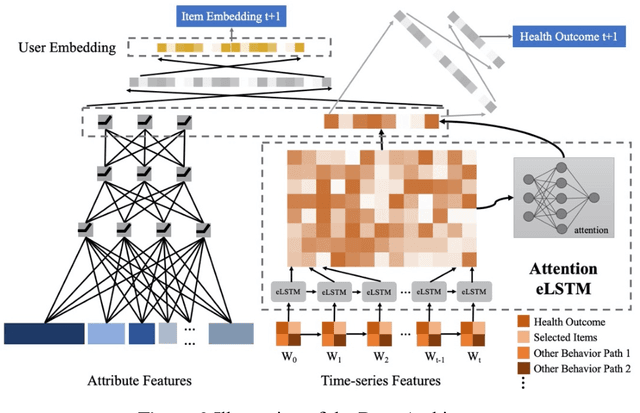

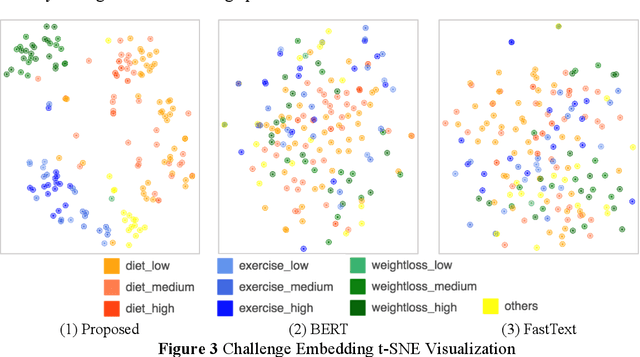
Abstract:Online healthcare communities provide users with various healthcare interventions to promote healthy behavior and improve adherence. When faced with too many intervention choices, however, individuals may find it difficult to decide which option to take, especially when they lack the experience or knowledge to evaluate different options. The choice overload issue may negatively affect users' engagement in health management. In this study, we take a design-science perspective to propose a recommendation framework that helps users to select healthcare interventions. Taking into account that users' health behaviors can be highly dynamic and diverse, we propose a multi-armed bandit (MAB)-driven recommendation framework, which enables us to adaptively learn users' preference variations while promoting recommendation diversity in the meantime. To better adapt an MAB to the healthcare context, we synthesize two innovative model components based on prominent health theories. The first component is a deep-learning-based feature engineering procedure, which is designed to learn crucial recommendation contexts in regard to users' sequential health histories, health-management experiences, preferences, and intrinsic attributes of healthcare interventions. The second component is a diversity constraint, which structurally diversifies recommendations in different dimensions to provide users with well-rounded support. We apply our approach to an online weight management context and evaluate it rigorously through a series of experiments. Our results demonstrate that each of the design components is effective and that our recommendation design outperforms a wide range of state-of-the-art recommendation systems. Our study contributes to the research on the application of business intelligence and has implications for multiple stakeholders, including online healthcare platforms, policymakers, and users.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge