Tomasz Kloda
Strict Partitioning for Sporadic Rigid Gang Tasks
Mar 15, 2024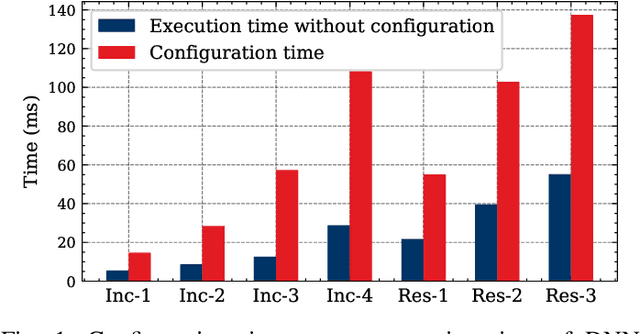

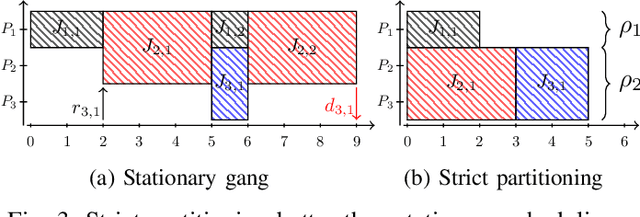
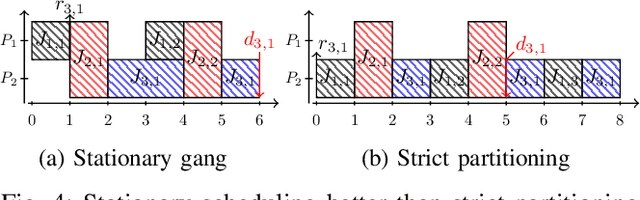
Abstract:The rigid gang task model is based on the idea of executing multiple threads simultaneously on a fixed number of processors to increase efficiency and performance. Although there is extensive literature on global rigid gang scheduling, partitioned approaches have several practical advantages (e.g., task isolation and reduced scheduling overheads). In this paper, we propose a new partitioned scheduling strategy for rigid gang tasks, named strict partitioning. The method creates disjoint partitions of tasks and processors to avoid inter-partition interference. Moreover, it tries to assign tasks with similar volumes (i.e., parallelisms) to the same partition so that the intra-partition interference can be reduced. Within each partition, the tasks can be scheduled using any type of scheduler, which allows the use of a less pessimistic schedulability test. Extensive synthetic experiments and a case study based on Edge TPU benchmarks show that strict partitioning achieves better schedulability performance than state-of-the-art global gang schedulability analyses for both preemptive and non-preemptive rigid gang task sets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge