Timur Mamedov
ReText: Text Boosts Generalization in Image-Based Person Re-identification
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Generalizable image-based person re-identification (Re-ID) aims to recognize individuals across cameras in unseen domains without retraining. While multiple existing approaches address the domain gap through complex architectures, recent findings indicate that better generalization can be achieved by stylistically diverse single-camera data. Although this data is easy to collect, it lacks complexity due to minimal cross-view variation. We propose ReText, a novel method trained on a mixture of multi-camera Re-ID data and single-camera data, where the latter is complemented by textual descriptions to enrich semantic cues. During training, ReText jointly optimizes three tasks: (1) Re-ID on multi-camera data, (2) image-text matching, and (3) image reconstruction guided by text on single-camera data. Experiments demonstrate that ReText achieves strong generalization and significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods on cross-domain Re-ID benchmarks. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to explore multimodal joint learning on a mixture of multi-camera and single-camera data in image-based person Re-ID.
ReMix: Training Generalized Person Re-identification on a Mixture of Data
Oct 29, 2024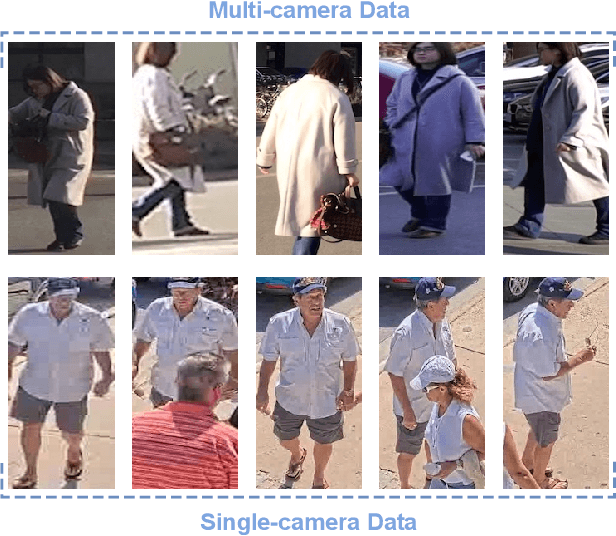
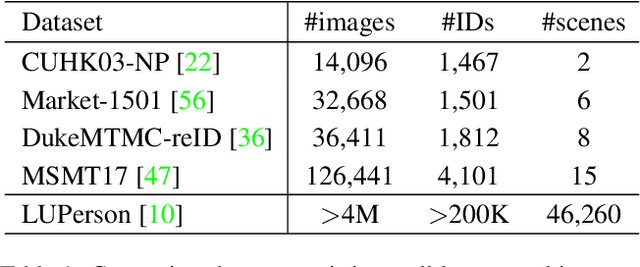
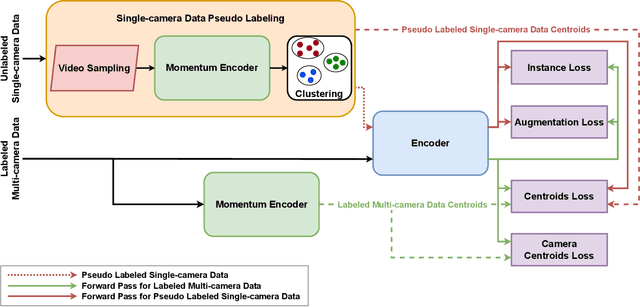
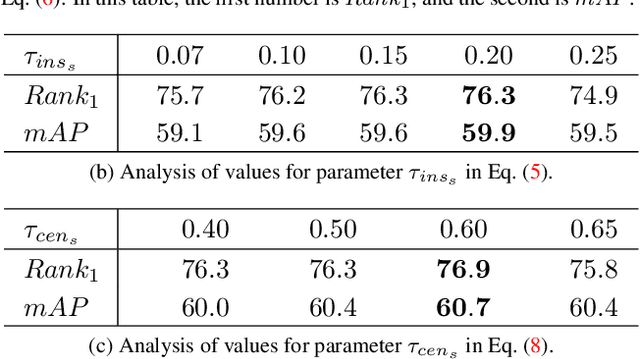
Abstract:Modern person re-identification (Re-ID) methods have a weak generalization ability and experience a major accuracy drop when capturing environments change. This is because existing multi-camera Re-ID datasets are limited in size and diversity, since such data is difficult to obtain. At the same time, enormous volumes of unlabeled single-camera records are available. Such data can be easily collected, and therefore, it is more diverse. Currently, single-camera data is used only for self-supervised pre-training of Re-ID methods. However, the diversity of single-camera data is suppressed by fine-tuning on limited multi-camera data after pre-training. In this paper, we propose ReMix, a generalized Re-ID method jointly trained on a mixture of limited labeled multi-camera and large unlabeled single-camera data. Effective training of our method is achieved through a novel data sampling strategy and new loss functions that are adapted for joint use with both types of data. Experiments show that ReMix has a high generalization ability and outperforms state-of-the-art methods in generalizable person Re-ID. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work that explores joint training on a mixture of multi-camera and single-camera data in person Re-ID.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge