Tien-Yu Chang
CAAP: Class-Dependent Automatic Data Augmentation Based On Adaptive Policies For Time Series
Apr 01, 2024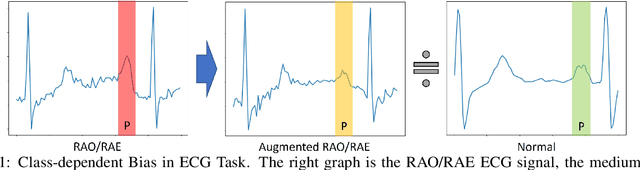
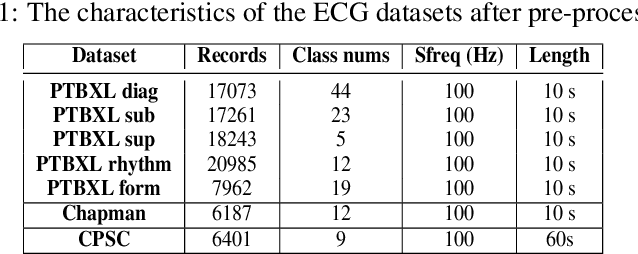
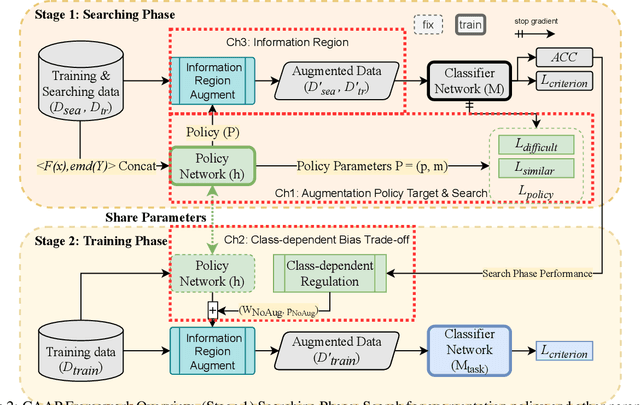

Abstract:Data Augmentation is a common technique used to enhance the performance of deep learning models by expanding the training dataset. Automatic Data Augmentation (ADA) methods are getting popular because of their capacity to generate policies for various datasets. However, existing ADA methods primarily focused on overall performance improvement, neglecting the problem of class-dependent bias that leads to performance reduction in specific classes. This bias poses significant challenges when deploying models in real-world applications. Furthermore, ADA for time series remains an underexplored domain, highlighting the need for advancements in this field. In particular, applying ADA techniques to vital signals like an electrocardiogram (ECG) is a compelling example due to its potential in medical domains such as heart disease diagnostics. We propose a novel deep learning-based approach called Class-dependent Automatic Adaptive Policies (CAAP) framework to overcome the notable class-dependent bias problem while maintaining the overall improvement in time-series data augmentation. Specifically, we utilize the policy network to generate effective sample-wise policies with balanced difficulty through class and feature information extraction. Second, we design the augmentation probability regulation method to minimize class-dependent bias. Third, we introduce the information region concepts into the ADA framework to preserve essential regions in the sample. Through a series of experiments on real-world ECG datasets, we demonstrate that CAAP outperforms representative methods in achieving lower class-dependent bias combined with superior overall performance. These results highlight the reliability of CAAP as a promising ADA method for time series modeling that fits for the demands of real-world applications.
FLAG: Fast Label-Adaptive Aggregation for Multi-label Classification in Federated Learning
Feb 27, 2023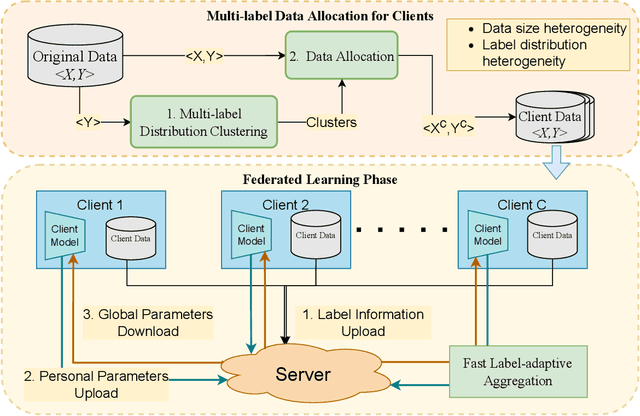
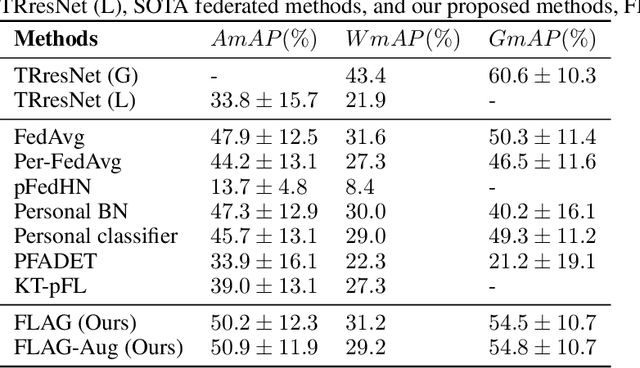
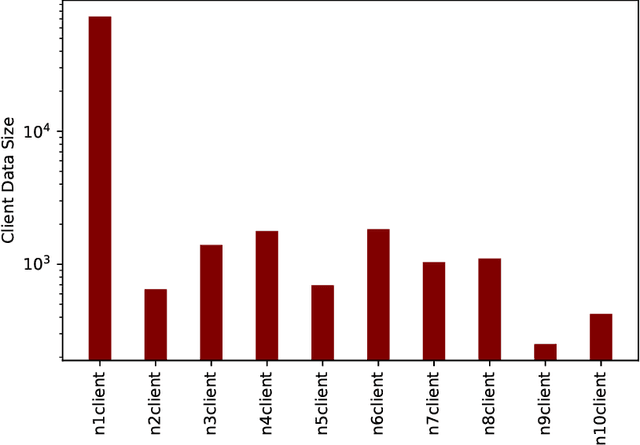
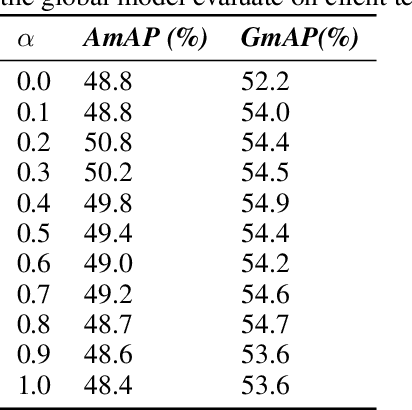
Abstract:Federated learning aims to share private data to maximize the data utility without privacy leakage. Previous federated learning research mainly focuses on multi-class classification problems. However, multi-label classification is a crucial research problem close to real-world data properties. Nevertheless, a limited number of federated learning studies explore this research problem. Existing studies of multi-label federated learning did not consider the characteristics of multi-label data, i.e., they used the concept of multi-class classification to verify their methods' performance, which means it will not be feasible to apply their methods to real-world applications. Therefore, this study proposed a new multi-label federated learning framework with a Clustering-based Multi-label Data Allocation (CMDA) and a novel aggregation method, Fast Label-Adaptive Aggregation (FLAG), for multi-label classification in the federated learning environment. The experimental results demonstrate that our methods only need less than 50\% of training epochs and communication rounds to surpass the performance of state-of-the-art federated learning methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge